Modulation of human polymorphonuclear neutrophil function by macrolides: preliminary data concerning dirithromycin.
M T Labro, J el Benna, H Abdelghaffar
Index: J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 31 Suppl C , 51-64, (1993)
Full Text: HTML
Abstract
Polymorphonuclear neutrophils (PMN) play a prominent role in the host response to infectious diseases. One major bactericidal mechanism used by these cells is the production of reactive oxygen species during what is referred to as the oxidative burst. However, excessive oxidant generation can also be involved in cell and tissue damage associated with severe inflammatory reactions. Macrolide antibiotics are able to penetrate and concentrate within phagocytes and have been successfully used to treat infections due to facultative intracellular pathogens. However, intracellular accumulation of macrolides with possible alkalinization of cellular compartments may interfere with normal cell function. In-vitro and ex-vivo data suggest that macrolides affect various phagocytic functions. This paper presents an overview of the published data concerning the modulation of neutrophil function by macrolides. Preliminary data concerning the in-vitro modulation of the neutrophil oxidative burst by dirithromycin and its metabolite, erythromycylamine, are also discussed.
Related Compounds
| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Molecular Formula | Articles |
|---|---|---|---|
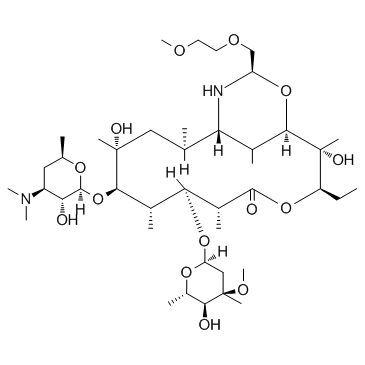 |
Dirithromycin
CAS:62013-04-1 |
C42H78N2O14 |
|
The new macrolide antibiotics: azithromycin, clarithromycin,...
1992-01-01 [Ann. Pharmacother. 26(1) , 46-55, (1992)] |
|
Pharmacokinetics of dirithromycin.
1993-03-01 [J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 31 Suppl C , 65-75, (1993)] |
|
Macrolide - induced clinically relevant drug interactions wi...
2000-10-01 [.PubMed ID] |
|
Dirithromycin. A review of its antimicrobial activity, pharm...
1994-10-01 [Drugs 48(4) , 599-616, (1994)] |
|
Drug interactions of macrolides: emphasis on dirithromycin.
1997-03-01 [Ann. Pharmacother. 31(3) , 349-56, (1997)] |