Alteration of hepatic carboxylesterase activity by soman: inhibition in vitro and enhancement in vivo.
M C Castle
Index: Xenobiotica 19(1) , 115-21, (1989)
Full Text: HTML
Abstract
1. Hydrolysis of the drug esters procaine, chloramphenicol succinate, and prednisolone succinate was studied. Addition of soman to guinea pig liver microsomes caused a dose-dependent inhibition of hydrolysis of all three substrates; at the highest soman concentration (1 microM), ester hydrolysis was totally abolished. 2. Ester hydrolysis was also measured in liver microsomes from guinea pigs pretreated with soman at a low dose (10% of LD50) or at a high dose (90% of LD50) either 1 h or 12 h before killing. Plasma-cholinesterase activity was decreased in all pretreated animals. Liver carboxylesterase activity, measured with the three drug substrates and by hydrolysis of 4-nitrophenyl acetate was increased by all pretreatments. 3. This enhancing effect varies with the substrate and increases with dose of soman. The 12 h pretreatment produced a greater increase in activity than did the 1 h pretreatment. 4. These studies indicate that soman is a potent inhibitor of carboxylesterase activity in vitro but increases the activity of the liver enzyme when administered in vivo.
Related Compounds
| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Molecular Formula | Articles |
|---|---|---|---|
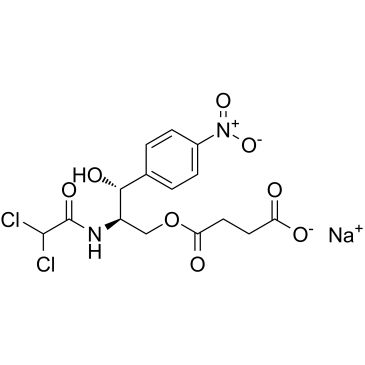 |
Chloramphenicol sodium succinate
CAS:982-57-0 |
C15H15Cl2N2NaO8 |
|
The myelotoxicity of chloramphenicol: in vitro and in vivo s...
1998-01-01 [Hum. Exp. Toxicol. 17(1) , 8-17, (1998)] |
|
A commercial enzyme immunoassay method (EMIT) compared with ...
1988-09-01 [Clin. Chem. 34(9) , 1872-5, (1988)] |
|
Chloramphenicol succinate, a competitive substrate and inhib...
2004-08-01 [Toxicol. In Vitro 18(4) , 441-7, (2004)] |
|
Fluorometric quantitation of broth-cultured mycoplasmas by u...
1993-05-01 [J. Clin. Microbiol. 31(5) , 1303-7, (1993)] |
|
Metabolism of chloramphenicol succinate in human bone marrow...
2000-08-01 [Eur. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 56(5) , 405-9, (2000)] |