A commercial enzyme immunoassay method (EMIT) compared with liquid chromatography and bioassay methods for measurement of chloramphenicol.
J G Schwartz, D T Casto, S Ayo, J J Carnahan, J H Jorgensen
Index: Clin. Chem. 34(9) , 1872-5, (1988)
Full Text: HTML
Abstract
A new enzyme immunoassay method (EMIT; Syva Co.) was compared with conventional high-performance liquid chromatography (HPLC) and agar-diffusion bioassay methods for measurement of chloramphenicol in human serum. Forty-nine serum samples were assayed by each of the three methods. Excellent correlation was observed between values by EMIT and by the two conventional methods (r = 0.986 and 0.961). Precision was acceptable (CV less than 5%) with EMIT. Assay of samples containing chloramphenicol glucuronide and chloramphenicol succinate demonstrated that EMIT recognizes only the biologically active (base) form of the drug. The capability to test serum samples as small as 0.2 mL, adaptation to widely available instrumentation, and provision of rapid results are principal advantages of the EMIT method for routine chloramphenicol measurements.
Related Compounds
| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Molecular Formula | Articles |
|---|---|---|---|
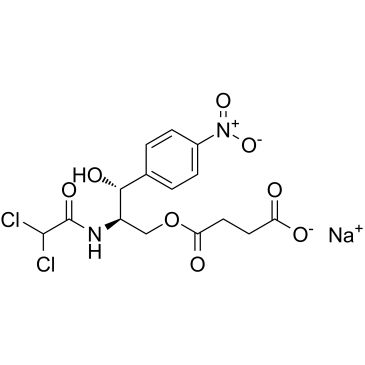 |
Chloramphenicol sodium succinate
CAS:982-57-0 |
C15H15Cl2N2NaO8 |
|
The myelotoxicity of chloramphenicol: in vitro and in vivo s...
1998-01-01 [Hum. Exp. Toxicol. 17(1) , 8-17, (1998)] |
|
Chloramphenicol succinate, a competitive substrate and inhib...
2004-08-01 [Toxicol. In Vitro 18(4) , 441-7, (2004)] |
|
Fluorometric quantitation of broth-cultured mycoplasmas by u...
1993-05-01 [J. Clin. Microbiol. 31(5) , 1303-7, (1993)] |
|
Metabolism of chloramphenicol succinate in human bone marrow...
2000-08-01 [Eur. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 56(5) , 405-9, (2000)] |
|
Haemotoxicity of chloramphenicol succinate in the CD-1 mouse...
1999-09-01 [Hum. Exp. Toxicol. 18(9) , 566-76, (1999)] |