Analysis of molecular epidemiologic characteristics of extended-spectrum β-lactamase (ESBL)-producing Escherichia coli colonizing feces in hospital patients and community dwellers in a Japanese city.
Akihiro Nakamura, Masaru Komatsu, Nobuyoshi Noguchi, Yuki Ohno, Eriko Hashimoto, Hiroko Matsutani, Noriyuki Abe, Saori Fukuda, Hisashi Kohno, Fumihiko Nakamura, Shuji Matsuo, Seiji Kawano
Index: J. Infect. Chemother. 22 , 102-7, (2016)
Full Text: HTML
Abstract
Infectious diseases caused by extended-spectrum β-lactamase (ESBL)-producing Escherichia coli are prevalent because of nosocomial infection. In addition, colonization of ESBL-producing E. coli in the intestinal tract of community dwellers due to the contamination of meat or environmental water is assumed to be one of the sources, but the causes have not been clarified. To analyze these factors, we investigated the difference in clonal groups using a combination of phylogenetic groups and multilocus sequence typing of ESBL-producing E. coli, which were obtained from the feces of an inpatient group in our hospital and a community-dwelling group living in a Japanese city. The carriage rate of ESBL-producing E. coli in the inpatient group was 12.5% (32/257), similar to that of 8.5% (42/496) in the community dwellers (P = 0.082). Of the ESBL clonal groups detected from the community dwellers, 52% (22/42) were clonal groups, including D-ST1485, D-ST70, D-ST2847, B2-ST550, B2-ST3510, A-ST93, A-ST580, A-ST716 and B1-ST2787, that have not been detected from human pathogens, meat, companion animals and environmental water, whereas all clonal groups detected from the inpatients were those that had already been reported. The rate of fluoroquinolone-resistant ESBL clonal groups colonizing the intestinal tract of the inpatient group rose as the number of hospital days increased. These results indicated that different factors were related to colonization of ESBL-producing E. coli in the feces of the inpatient group and the community-dwelling group.Copyright © 2015 Japanese Society of Chemotherapy and The Japanese Association for Infectious Diseases. Published by Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Related Compounds
| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Molecular Formula | Articles |
|---|---|---|---|
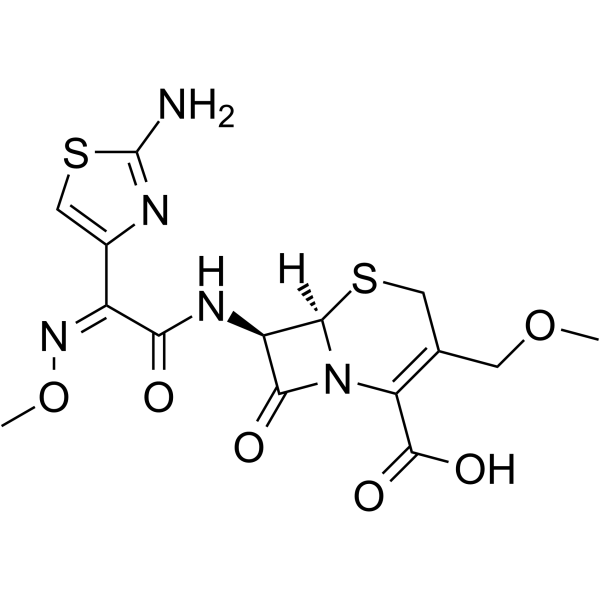 |
cefpodoxime
CAS:80210-62-4 |
C15H17N5O6S2 |
|
Isolation of Escherichia coli strains with AcrAB-TolC efflux...
2014-07-01 [J. Vet. Med. Sci. 76(7) , 937-45, (2014)] |
|
Increase in resistance to extended-spectrum cephalosporins i...
2015-01-01 [PLoS ONE 10(2) , e0116927, (2015)] |
|
Cephalosporinases associated with outer membrane vesicles re...
2015-03-01 [J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 70(3) , 701-9, (2015)] |
|
Oral bioavailability: issues and solutions via nanoformulati...
2015-04-01 [Clin. Pharmacokinet. 54(4) , 325-57, (2015)] |
|
Molecular typing and genetic environment of the blaKPC gene ...
[J Glob Antimicrob Resist 4 , 28-34, (2016)] |