Identification of promoter and stringent regulation of transcription of the fabH, fabD and fabG genes encoding fatty acid biosynthetic enzymes of Escherichia coli.
S M Podkovyrov, T J Larson
Index: Nucleic Acids Res. 24(9) , 1747-52, (1996)
Full Text: HTML
Abstract
In Escherichia coli, amino acid starvation results in the coordinate inhibition of a variety of metabolic activities, including fatty acid and phospholipid biosynthesis. By using primer extension analysis we identified the fabH promoter responsible for transcription of the fabH, fabD and fabG genes encoding fatty acid biosynthetic enzymes. The response of the fabH promoter to amino acid starvation was determined in vivo. Transcripts originating from the fabH promoter were quantified by employing a ribonuclease protection assay. The fabH promoter was subject to relA-dependent stringent control and was repressed approximately 4-fold upon amino acid starvation. The results suggest that inhibition of transcription initiation of lipid biosynthetic genes in starved cells contributes to the stringent control of lipid biosynthesis.
Related Compounds
| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Molecular Formula | Articles |
|---|---|---|---|
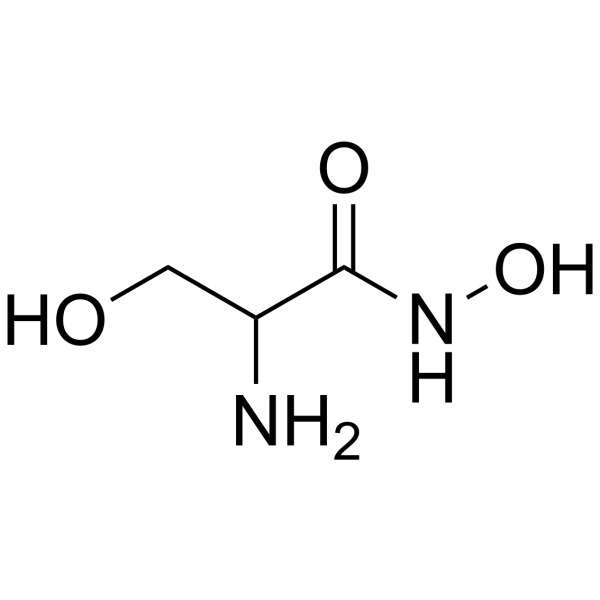 |
DL-Serine hydroxamate
CAS:55779-32-3 |
C3H8N2O3 |
|
Selective inhibition of divergent seryl-tRNA synthetases by ...
2005-08-15 [FEBS Lett. 579(20) , 4344-8, (2005)] |
|
Genome conformation capture reveals that the Escherichia col...
2013-07-01 [Nucleic Acids Res. 41(12) , 6058-71, (2013)] |
|
Serine hydroxamate and the transcriptome of high cell densit...
2009-05-01 [Appl. Biochem. Biotechnol. 157(2) , 124-39, (2009)] |
|
Global gene expression during stringent response in Coryneba...
2006-01-01 [BMC Genomics 7 , 230, (2006)] |
|
Transcription profiling of the stringent response in Escheri...
2008-02-01 [J. Bacteriol. 190(3) , 1084-96, (2008)] |