| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Articles |
|---|---|---|
 |
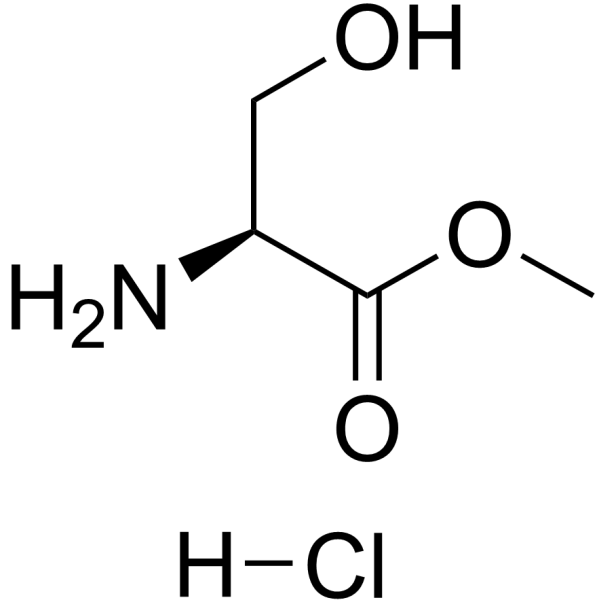
Methyl serinate hydrochloride
CAS:5619-04-5 |
|
 |
H-Ser-Ome·HCl
CAS:5680-80-8 |
|
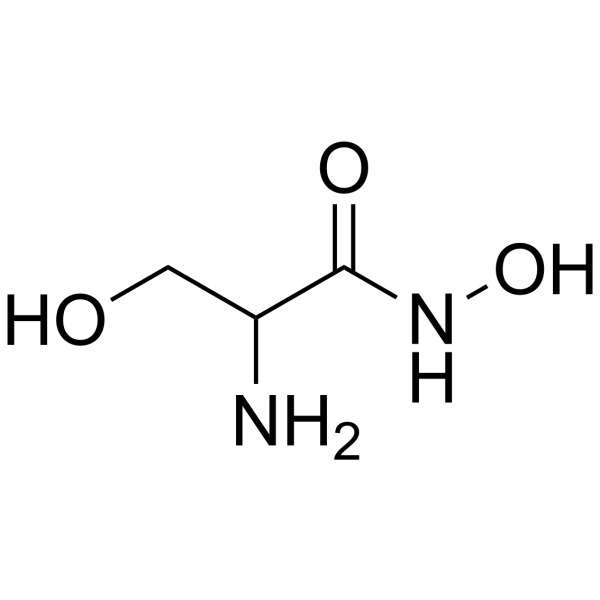 |
DL-Serine hydroxamate
CAS:55779-32-3 |
|
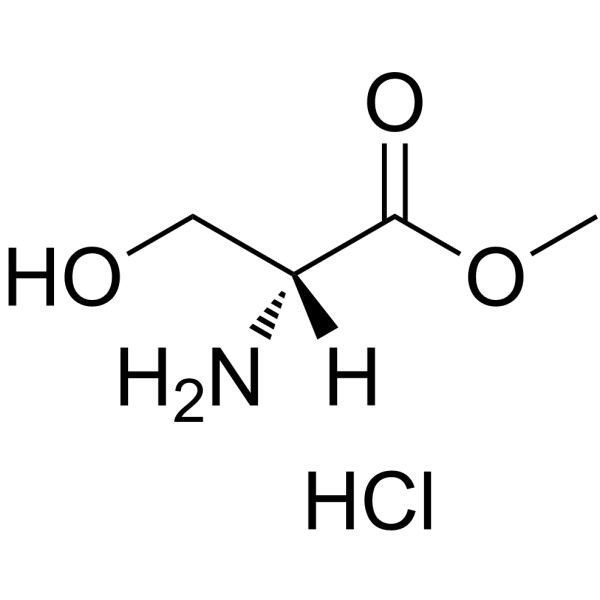 |
H-D-Ser-OMe.HCl
CAS:5874-57-7 |