Hydrolysis of non-cognate aminoacyl-adenylates by a class II aminoacyl-tRNA synthetase lacking an editing domain.
Ita Gruic-Sovulj, Jasmina Rokov-Plavec, Ivana Weygand-Durasevic
Index: FEBS Lett. 581(26) , 5110-4, (2007)
Full Text: HTML
Abstract
Aminoacyl-tRNA synthetases, a group of enzymes catalyzing aminoacyl-tRNA formation, may possess inherent editing activity to clear mistakes arising through the selection of non-cognate amino acid. It is generally assumed that both editing substrates, non-cognate aminoacyl-adenylate and misacylated tRNA, are hydrolyzed at the same editing domain, distant from the active site. Here, we present the first example of an aminoacyl-tRNA synthetase (seryl-tRNA synthetase) that naturally lacks an editing domain, but possesses a hydrolytic activity toward non-cognate aminoacyl-adenylates. Our data reveal that tRNA-independent pre-transfer editing may proceed within the enzyme active site without shuttling the non-cognate aminoacyl-adenylate intermediate to the remote editing site.
Related Compounds
| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Molecular Formula | Articles |
|---|---|---|---|
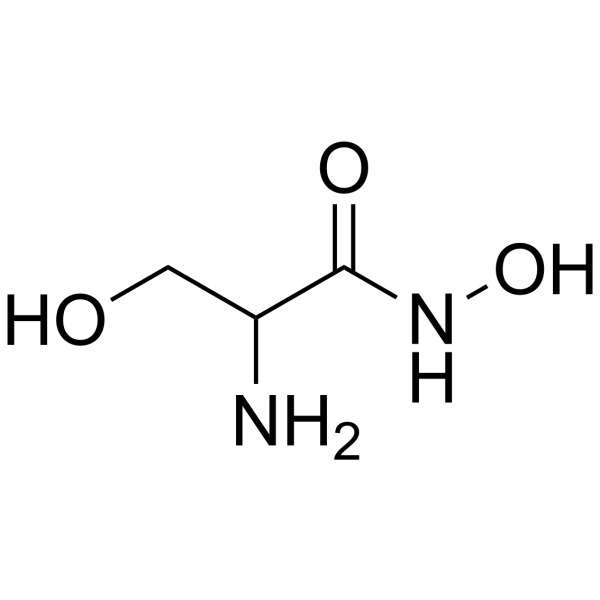 |
DL-Serine hydroxamate
CAS:55779-32-3 |
C3H8N2O3 |
|
Selective inhibition of divergent seryl-tRNA synthetases by ...
2005-08-15 [FEBS Lett. 579(20) , 4344-8, (2005)] |
|
Genome conformation capture reveals that the Escherichia col...
2013-07-01 [Nucleic Acids Res. 41(12) , 6058-71, (2013)] |
|
Serine hydroxamate and the transcriptome of high cell densit...
2009-05-01 [Appl. Biochem. Biotechnol. 157(2) , 124-39, (2009)] |
|
Global gene expression during stringent response in Coryneba...
2006-01-01 [BMC Genomics 7 , 230, (2006)] |
|
Transcription profiling of the stringent response in Escheri...
2008-02-01 [J. Bacteriol. 190(3) , 1084-96, (2008)] |