Mitochondria targeting of non-peroxidizable triphenylphosphonium conjugated oleic acid protects mouse embryonic cells against apoptosis: role of cardiolipin remodeling.
Yulia Y Tyurina, Muhammad A Tungekar, Mi-Yeon Jung, Vladimir A Tyurin, Joel S Greenberger, Detcho A Stoyanovsky, Valerian E Kagan
Index: FEBS Lett. 586(3) , 235-41, (2012)
Full Text: HTML
Abstract
Peroxidation of cardiolipin in mitochondria is essential for the execution of apoptosis. We suggested that integration of oleic acid into cardiolipin generates non-oxidizable cardiolipin species hence protects cells against apoptosis. We synthesized mitochondria-targeted triphenylphosphonium oleic acid ester. Using lipidomics analysis we found that pretreatment of mouse embryonic cells with triphenylphosphonium oleic acid ester resulted in decreased contents of polyunsaturated cardiolipins and elevation of its species containing oleic acid residues. This caused suppression of apoptosis induced by actinomycin D. Triacsin C, an inhibitor of acyl-CoA synthase, blocked integration of oleic acid into cardiolipin and restored cell sensitivity to apoptosis.Copyright © 2011 Federation of European Biochemical Societies. Published by Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
Related Compounds
| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Molecular Formula | Articles |
|---|---|---|---|
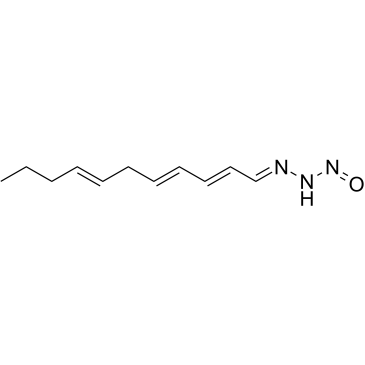 |
Triacsin C from Streptomyces sp.
CAS:76896-80-5 |
C11H17N3O |
|
Acyl-CoA synthetase as a cancer survival factor: its inhibit...
2009-08-01 [Cancer Sci. 100(8) , 1556-62, (2009)] |
|
Human intestinal acyl-CoA synthetase 5 is sensitive to the i...
2011-11-28 [World J. Gastroenterol. 17(44) , 4883-9, (2011)] |
|
Diacylglycerol enrichment of endoplasmic reticulum or lipid ...
2009-11-06 [J. Thorac. Cardiovasc. Surg. 284 , 30941-8, (2009)] |
|
Selective and potent in vitro antimalarial activities found ...
2007-03-01 [J. Antibiot. 60(3) , 220-2, (2007)] |
|
Intracellular fatty acids suppress β-adrenergic induction of...
2011-07-01 [Am. J. Physiol. Endocrinol. Metab. 301(1) , E122-31, (2011)] |