| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Articles |
|---|---|---|
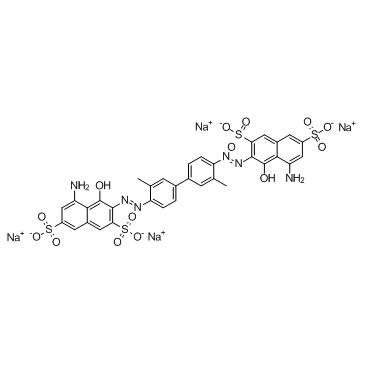 |
Direct Blue 14
CAS:72-57-1 |
|
 |
Hemicholinium 3
CAS:312-45-8 |
|
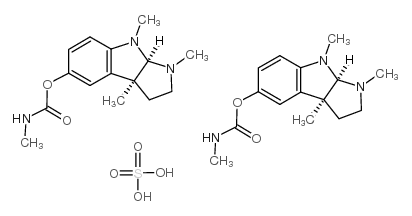 |
Physostigmine hemisulfate
CAS:64-47-1 |
|
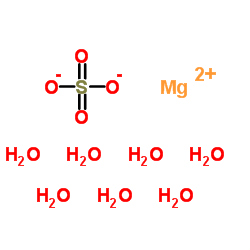 |
magnesium sulfate heptahydrate
CAS:10034-99-8 |