Selective reduction in alpha-hydroxypalmitic acid-containing sphingomyelin and concurrent increase in hydroxylated ceramides in murine skin tumors induced by an initiation-promotion regimen.
Y Kitano, Y Iwamori, K Kiguchi, J DiGiovanni, T Takahashi, K Kasama, T Niwa, K Harii, M Iwamori
Index: Jpn. J. Cancer Res. 87(5) , 437-41, (1996)
Full Text: HTML
Abstract
The sphingomyelin cycle is activated to accumulate ceramides in the process of epidermal differentiation. We found that sphingomyelin in the epidermis of 4 different murine strains gave three bands on TLC, the lower band containing alpha-hydroxypalmitic acid (C16h:0(alpha)). However, in the papillomas induced in the skin of SENCAR and SSIN mice by initiation with 7,12-dimethylbenz[a]anthracene followed by promotion with 12-O-tetradecanoylphorbol acetate, the concentration of C16h:0(alpha)-containing sphingomyelin was selectively diminished with a concomitant increase in the concentrations of the ceramides containing alpha-hydroxy fatty acids. These findings indicate a possible involvement of the selective hydrolysis of alpha-hydroxy fatty acid-containing sphingomyelin in the process of tumorigenesis in mouse skin.
Related Compounds
| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Molecular Formula | Articles |
|---|---|---|---|
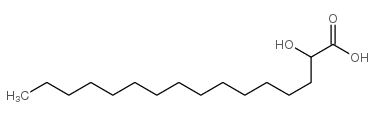 |
2-hydroxy Palmitic Acid
CAS:764-67-0 |
C16H32O3 |
|
Synthesis of lipophilic 2-oxoamides based on gamma-aminobuty...
2007-10-01 [J. Pept. Sci. 13 , 634-641, (2007)] |
|
Determination of glucosylceramide contents in crop tissues a...
2005-06-01 [Bioresour. Technol. 96 , 1089-1092, (2005)] |
|
The effects of hydroxy fatty acids on the hyphal branching o...
2011-01-01 [Fungal Biol. 115 , 351-358, (2011)] |
|
Flip-flop of hydroxy fatty acids across the membrane as moni...
2008-05-01 [Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1778 , 1292-1297, (2008)] |
|
Transport of fatty acids across membranes by the diffusion m...
1999-01-01 [Prostaglandins Leukot. Essent. Fatty Acids 60 , 291-297, (1999)] |