Decrease in adherence of bacteria and yeasts to human mucosal epithelial cells by noxythiolin in vitro.
S P Gorman, D F McCafferty, A D Woolfson, L Anderson
Index: J. Appl. Bacteriol. 60(4) , 311-7, (1986)
Full Text: HTML
Abstract
Adherence of buccal and vaginal isolates of Candida albicans to buccal epithelial cells and the adherence of urine isolates of Escherichia coli and Staphylococcus saprophyticus to uroepithelial cells was quantified by light microscopy. The antimicrobial agent noxythiolin reduced the adherence of these micro-organisms in both exponential and stationary growth phases. Adherence of both the blastospore and pseudohyphal forms of C. albicans was reduced. Treatment of epithelial cells and/or micro-organisms with noxythiolin resulted in decreased adherence. No anti-adherence effect was observed with formaldehyde and N-methylthiourea, the degradative products of noxythiolin.
Related Compounds
| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Molecular Formula | Articles |
|---|---|---|---|
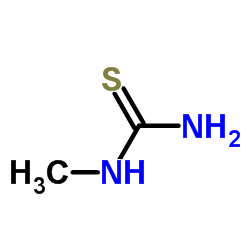 |
N-Methylthiourea
CAS:598-52-7 |
C2H6N2S |
|
Endothelial nitric oxide synthase deficient mice are protect...
2015-01-01 [PLoS ONE 10(3) , e0119918, (2015)] |
|
Metabolism of 4-[1-(2-fluoro-4-biphenylyl)ethyl]-2-methylami...
1997-01-01 [Eur. J. Drug Metab. Pharmacokinet. 22(1) , 25-33, (1997)] |
|
[Proper use of noxythiolin: an experimental rat study on int...
1980-01-01 [Therapie. 35(3) , 409-12, (1980)] |
|
PPAR-γ regulates carnitine homeostasis and mitochondrial fun...
2012-01-01 [PLoS ONE 7(9) , e41555, (2012)] |
|
Ameliorative effects of taurine against methimazole-induced ...
2012-12-01 [Sci. Pharm. 80 , 987-99, (2012)] |