Novel microemulsion in situ electrolyte-triggered gelling system for ophthalmic delivery of lipophilic cyclosporine A: in vitro and in vivo results.
Li Gan, Yong Gan, Chunliu Zhu, Xinxin Zhang, Jiabi Zhu
Index: Int. J. Pharm. 365(1-2) , 143-149, (2009)
Full Text: HTML
Abstract
The objective of the present study was to design a novel microemulsion in situ electrolyte-triggered gelling system for ophthalmic delivery of a lipophilic drug, cyclosporine A (CsA). A CsA-loaded microemulsion was prepared using castor oil, Solutol HS 15 (surfactant), glycerol and water. This microemulsion was then dispersed in a Kelcogel solution to form the final microemulsion in situ electrolyte-triggered gelling system. In vitro, the viscosity of the CsA microemulsion Kelcogel system increased dramatically on dilution with artificial tear fluid and exhibited pseudo-plastic rheology. In vivo results revealed that the AUC(0-->32 h) of corneal CsA for the microemulsion Kelcogel system was approximately three-fold greater than for a CsA emulsion. Moreover, at 32 h after administration, CsA concentrations delivered by the microemulsion Kelcogel system remained at therapeutic levels in the cornea. This CsA microemulsion in situ electrolyte-triggered gelling system might provide an alternative approach to deliver prolonged precorneal residence time of CsA for preventing cornea allograft rejection.
Related Compounds
| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Molecular Formula | Articles |
|---|---|---|---|
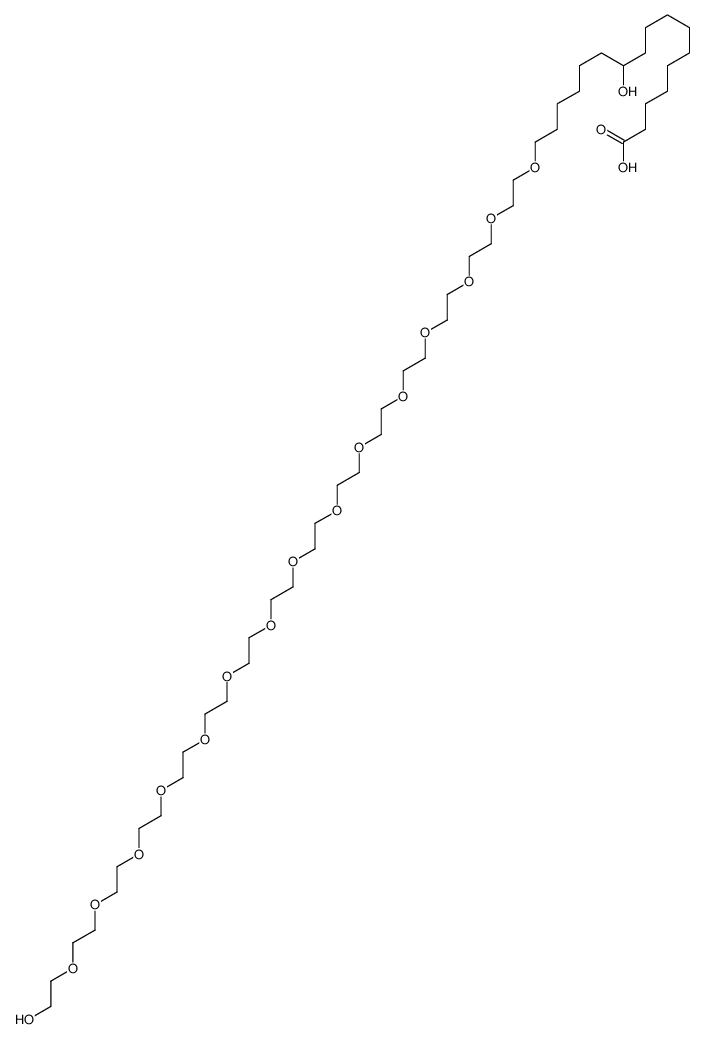 |
Polyoxyl 15 hydroxystearate
CAS:70142-34-6 |
C47H94O19 |
|
Detrimental role of the EP1 prostanoid receptor in blood-bra...
2015-01-01 [Sci. Rep. 5 , 17956, (2015)] |
|
Solutol HS 15, nontoxic polyoxyethylene esters of 12-hydroxy...
1991-02-01 [Cancer Res. 51 , 897-902, (1991)] |
|
The encapsulation of DNA molecules within biomimetic lipid n...
2009-06-01 [Biomaterials 30(18) , 3197-3204, (2009)] |
|
Emulsifiers' composition modulates venous irritation of the ...
2009-01-01 [AAPS PharmSci 10(3) , 1058-1064, (2009)] |
|
Ozone-Induced Hypertussive Responses in Rabbits and Guinea P...
2016-04-01 [J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 357 , 73-83, (2016)] |