| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Articles |
|---|---|---|
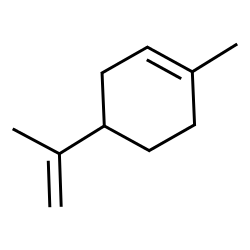 |
Orange sweet oil
CAS:8008-57-9 |
|
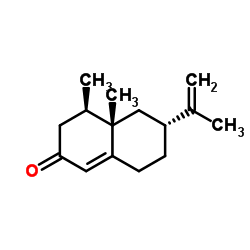 |
Nootkatone
CAS:4674-50-4 |