Trimethyl phosphite as a trap for alkoxy radicals formed from the ring opening of oxiranylcarbinyl radicals. Conversion to alkenes. Mechanistic applications to the study of C-C versus C-O ring cleavage.
Bangwei Ding, Wesley G Bentrude
Index: J. Am. Chem. Soc. 125(11) , 3248-59, (2003)
Full Text: HTML
Abstract
Trimethyl phosphite, (MeO)(3)P, is introduced as an efficient and selective trap in oxiranylcarbinyl radical (2) systems, formed from haloepoxides 8-13 under thermal AIBN/n-Bu(3)SnH conditions at about 80 degrees C. Initially, the transformations of 8-13, in the absence of phosphite, to allyl alcohol 7 and/or vinyl ether 5 were measured quantitatively (Table 1). Structural variations in the intermediate oxiranylcarbinyl (2), allyloxy (3), and vinyloxycarbinyl (4) radicals involve influences of the thermodynamics and kinetics of the C-O (2 --> 3, k(1)) and C-C (2 --> 4, k(2)) radical scission processes and readily account for the changes in the amounts of product vinyl ether (5) and allyl alcohol (7) formed. Added (MeO)(3)P is inert to vinyloxycarbinyl radical 4 and selectively and rapidly traps allyloxy radical 3, diverting it to trimethyl phosphate and allyl radical 6. Allyl radicals (6) dimerize or are trapped by n-Bu(3)SnH to give alkenes, formed from haloepoxides 8, 9, and 13 in 69-95% yields. Intermediate vinyloxycarbinyl radicals (4), in the presence or absence of (MeO)(3)P, are trapped by n-Bu(3)SnH to give vinyl ethers (5). The concentrations of (MeO)(3)P and n-Bu(3)SnH were varied independently, and the amounts of phosphate, vinyl ether (5), and/or alkene from haloepoxides 10, 11, and 13 were carefully monitored. The results reflect readily understood influences of changes in the structures of radicals 2-4, particularly as they influence the C-O (k(1)) and C-C (k(2)) cleavages of intermediate oxiranylcarbinyl radical 2 and their reverse (k(-1), k(-2)). Diversion by (MeO)(3)P of allyloxy radicals (3) from haloepoxides 11 and 12 fulfills a prior prediction that under conditions closer to kinetic control, products of C-O scission, not just those of C-C scission, may result. Thus, for oxiranylcarbinyl radicals from haloepoxides 11, 12, and 13, C-O scission (k(1), 2 --> 3) competes readily with C-C cleavage (k(2), 2 --> 4), even though C-C scission is favored thermodynamically.
Related Compounds
| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Molecular Formula | Articles |
|---|---|---|---|
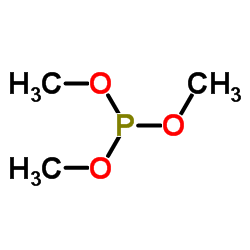 |
Trimethyl phosphite
CAS:121-45-9 |
C3H9O3P |
|
Interactions of multitargeted kinase inhibitors and nucleosi...
2015-01-01 [J. Chromatogr. A. 1421 , 154-61, (2015)] |
|
Rapid modification of the insect elicitor N-linolenoyl-gluta...
2010-01-01 [BMC Plant Biol. 10 , 164, (2010)] |
|
The functionalisation of saturated hydrocarbons--XXX. Model ...
1994-04-01 [Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2(4) , 259-66, (1994)] |
|
Surface characterization and platelet adhesion studies of pl...
1999-08-01 [Biomaterials 20(16) , 1439-47, (1999)] |
|
Teratological evaluation of trimethyl phosphite in the rat.
1984-01-01 [Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 72(1) , 119-23, (1984)] |