γ-Glutamylamines and neurodegenerative diseases.
Thomas M Jeitner, Kevin Battaile, Arthur J L Cooper
Index: Amino Acids 44(1) , 129-42, (2013)
Full Text: HTML
Abstract
Transglutaminases catalyze the formation of γ-glutamylamines utilizing glutamyl residues and amine-bearing compounds such as lysyl residues and polyamines. These γ-glutamylamines can be released from proteins by proteases in an intact form. The free γ-glutamylamines can be catabolized to 5-oxo-L-proline and the free amine by γ-glutamylamine cyclotransferase. Free γ-glutamylamines, however, accumulate in the CSF and affected areas of Huntington Disease brain. This observation suggests transglutaminase-derived γ-glutamylamines may play a more significant role in neurodegeneration than previously thought. The following monograph reviews the metabolism of γ-glutamylamines and examines the possibility that these species contribute to neurodegeneration.
Related Compounds
| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Molecular Formula | Articles |
|---|---|---|---|
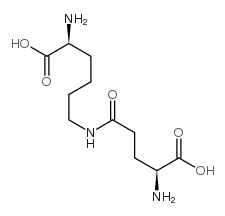 |
H-Glu(H-Lys-OH)-OH
CAS:17105-15-6 |
C11H21N3O5 |
|
In-vitro digestibility and amino acid composition of soy pro...
2009-01-01 [Int. J. Food Sci. Nutr. 60 Suppl 7 , 99-108, (2009)] |
|
Inhibition of transglutaminase activity reduces extracellula...
2004-11-12 [J. Biol. Chem. 279(46) , 47754-62, (2004)] |
|
Identification and quantification of epsilon-(gamma-glutamyl...
2005-04-20 [J. Agric. Food Chem. 53(8) , 2830-7, (2005)] |
|
Tissue transglutaminase: a mediator and predictor of chronic...
2004-06-15 [Transplantation 77(11) , 1667-75, (2004)] |
|
Tuft protein: protein cross-linking in enamel development.
2011-12-01 [Eur. J. Oral Sci. 119 Suppl 1 , 50-4, (2011)] |