Trans-Aconitic Acid in Range Grasses in Early Spring.
R Burau, P R Stout
Index: Science 150(3697) , 766-7, (1965)
Full Text: HTML
Abstract
trans-Aconitate ion, an inhibitor of the tricarboxylic acid cycle, was identified in range grasses as trans-aconitic acid, which was isolated in crystalline form. It occurs in surprisingly high concentrations in early-season forage grasses. Dry-weight concentrations of trans-aconitate vary with season and species; concentrations of between I and 2.5 percent are common in mixed pasture grasses, but are higher in certain species such as Hordeum leporinum (3.5 percent) and Phalaris tuberosa var. stenoptera (4.2 percent). Leaves of western larkspur (Delphinium hesperium) contain 12.2 percent trans-aconitate. trans-Aconitate may be partially responsible for nutritional disorders, such as grass tetany (hypomagnesemia), that occur in grazing cattle in early spring.
Related Compounds
| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Molecular Formula | Articles |
|---|---|---|---|
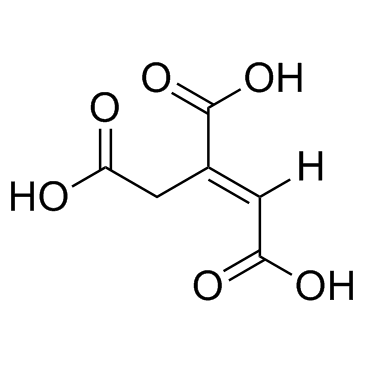 |
(E)-Aconitic Acid
CAS:4023-65-8 |
C6H6O6 |
|
HMDB: a knowledgebase for the human metabolome.
2009-01-01 [Nucleic Acids Res. 37(Database issue) , D603-10, (2009)] |
|
Prediction of skeletal muscle and fat mass in patients with ...
2012-01-01 [J. Nutr. 142(1) , 14-21, (2012)] |
|
SPE-NMR metabolite sub-profiling of urine.
2012-11-01 [Anal. Bioanal. Chem 404(8) , 2349-61, (2012)] |
|
Detection of autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease by...
2011-06-01 [Kidney Int. 79(11) , 1244-53, (2011)] |
|
Physiological and morphological adaptations of herbaceous pe...
2015-08-01 [Physiol. Plant. 154 , 511-25, (2015)] |