Involvement of peptidyl-prolyl isomerase Pin1 in the inhibitory effect of fluvastatin on endothelin-1-induced cardiomyocyte hypertrophy
Satoshi Sakai, Nobutake Shimojo, Taizo Kimura, Kazuko Tajiri, Hidekazu Maruyama, Satoshi Homma, Keisuke Kuga, Taro Mizutani, Kazutaka Aonuma, Takashi Miyauchi
Index: Life Sci. 102(2) , 98-104, (2014)
Full Text: HTML
Abstract
Aims Cardiac hypertrophy is elicited by endothelin (ET)-1 as well as other neurohumoral factors, hemodynamic overload, and oxidative stress; HMG-CoA reductase inhibitors (statins) were shown to inhibit cardiac hypertrophy partly via the anti-oxidative stress. One of their common intracellular pathways is the phosphorylation cascade of MEK signaling. Pin1 specifically isomerizes the phosphorylated protein with Ser/Thr-Pro bonds and regulates their activity through conformational changes. There is no report whether the Pin1 activation contributes to ET-1-induced cardiomyocyte hypertrophy and whether the Pin1 inactivation contributes to the inhibitory effect of statins. The aim of this study was to reveal these questions.
Related Compounds
| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Molecular Formula | Articles |
|---|---|---|---|
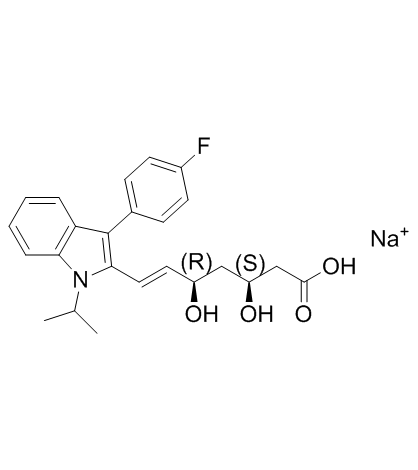 |
Fluvastatin Sodium
CAS:93957-55-2 |
C24H26FNNaO4+ |
|
Dehydroepiandrosterone sulfate, a useful endogenous probe fo...
2015-04-01 [Drug Metab. Pharmacokinet. 30(2) , 198-204, (2015)] |
|
3-Hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl coenzyme A reductase inhibitor (f...
2013-05-01 [APMIS 121(5) , 422-30, (2013)] |
|
The effects of different types of statins on proliferation a...
2013-11-01 [Eur. Rev. Med. Pharmacol. Sci. 17(21) , 2874-83, (2013)] |
|
Antithrombotic actions of statins involve PECAM-1 signaling.
2013-10-31 [Blood 122(18) , 3188-96, (2013)] |
|
Simvastatin inhibits the core promoter of the TXNRD1 gene an...
2013-01-04 [Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 430(1) , 90-4, (2013)] |