Enzymatic synthesis of a 2-O-alpha-D-glucopyranosyl cyclic tetrasaccharide by kojibiose phosphorylase.
Hikaru Watanabe, Takanobu Higashiyama, Hajime Aga, Tomoyuki Nishimoto, Michio Kubota, Shigeharu Fukuda, Masashi Kurimoto, Yoshio Tsujisaka
Index: Carbohydr. Res. 340(3) , 449-54, (2005)
Full Text: HTML
Abstract
The glucosyl transfer reaction of kojibiose phosphorylase (KPase) from Thermoanaerobacter brockii ATCC35047 was examined using cyclo-{-->6)-alpha-d-Glcp-(1-->3)-alpha-d-Glcp-(1-->6)-alpha-d-Glcp-(1-->3)-alpha-d-Glcp-(1-->} (CTS) as an acceptor. KPase produced four transfer products, saccharides 1-4. The structure of a major product, saccharide 4, was 2-O-alpha-d-glucopyranosyl-CTS, cyclo-{-->6)-alpha-d-Glcp-(1-->3)-alpha-d-Glcp-(1-->6)-[alpha-d-Glcp-(1-->2)]-alpha-d-Glcp-(1-->3)-alpha-d-Glcp-(1-->}. The other transfer products, saccharides 1-3, were 2-O-alpha-kojibiosyl-, 2-O-alpha-kojitriosyl-, and 2-O-alpha-kojitetraosyl-CTS, respectively. These results showed that KPase transferred a glucose residue to the C-2 position at the ring glucose residue of CTS. This enzyme also catalyzed the chain-extending reaction of the side chain of 2-O-alpha-d-glycopyranosyl-CTS.
Related Compounds
| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Molecular Formula | Articles |
|---|---|---|---|
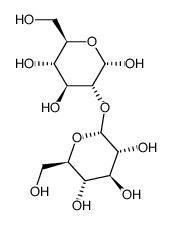 |
Kojibiose
CAS:2140-29-6 |
C12H22O11 |
|
Extracellular and cell-associated forms of Gluconobacter oxy...
2015-01-02 [Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 456(1) , 500-5, (2015)] |
|
Differentiation of Disaccharide Isomers by Temperature-Depen...
2015-09-01 [J. Am. Soc. Mass Spectrom. 26 , 1599-605, (2015)] |
|
Microbial Communities Can Be Described by Metabolic Structur...
2015-01-01 [PLoS ONE 10 , e0135868, (2015)] |
|
Transfer of oligosaccharide from oligosaccharide pyrophospho...
1985-07-15 [Experientia 41(7) , 928-9, (1985)] |
|
Acceptor recognition of kojibiose phosphorylase from Thermoa...
2006-05-01 [J. Biosci. Bioeng. 101(5) , 427-33, (2006)] |