Detection of degradation products of chemical warfare agents by highly porous molecularly imprinted microspheres.
Lucie Malosse, Pierrick Buvat, Dominique Adès, Alain Siove
Index: Analyst 133(5) , 588-95, (2008)
Full Text: HTML
Abstract
The multiplication of terrorist actions in the recent events is alarming and the detection of chemical warfare agents (CWAs) has become one of the highest research priorities in the fields of security and public health. The biomimetic properties of molecularly imprinted polymers (MIPs) render them attractive for molecular recognition as well as sensing purposes. The degradation products of easily hydrolysable organophosphorus nerve agents such as pinacolyl methylphosphonate (PMP), a hydrolysis by-product of soman, are often used as templates in MIP synthesis. In this study, we describe the first example of PMP-imprinted polymer microspheres synthesized by precipitation polymerization. This one-step process involves methacrylic acid (MAA) as the monomer and divinylbenzene (DVB) as the cross-linker, in a toluene/acetonitrile mixture. Subsequent morphological characterizations of the PMP-imprinted particles show that they have diameters between 1 and 10 mum (as opposed to 4-5 mum for the non-imprinted microspheres), surface areas of up to 680 m(2) g(-1) and high porosities with pore sizes smaller than 2 nm. The present investigation also evidences the imprinting effect via batch binding experiments and reports on the use of a novel fluorescence-based methodology, where 4-methylumbelliferone (4MU) is utilised as a sensing agent to determine the PMP concentration in solution.
Related Compounds
| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Molecular Formula | Articles |
|---|---|---|---|
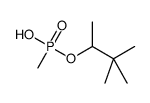 |
pinacolyl methylphosphonate
CAS:616-52-4 |
C7H17O3P |
|
On-line solid phase extraction-liquid chromatography-mass sp...
2013-01-25 [Anal. Chim. Acta 761 , 109-16, (2013)] |
|
Capillary ion electrophoresis screening of nerve agent degra...
1998-10-16 [J. Chromatogr. A. 824(1) , 125-34, (1998)] |
|
On-line solid-phase extraction liquid chromatography-continu...
1999-02-19 [J. Chromatogr. A. 833(2) , 169-79, (1999)] |
|
Derivatization of organophosphorus nerve agent degradation p...
2007-06-01 [Anal. Bioanal. Chem 388(4) , 809-23, (2007)] |
|
Inhibition of adenylyl cyclase by acyclic nucleoside phospho...
1999-12-03 [J. Biol. Chem. 274(49) , 34742-4, (1999)] |