Collagen-binding activity of Prevotella intermedia measured by a microtitre plate adherence assay.
D Grenier
Index: Microbiology 142 ( Pt 6) , 1537-41, (1996)
Full Text: HTML
Abstract
The ability of Prevotella intermedia to bind type I collagen was investigated. A simple method in which bacterial cells were allowed to attach to collagen-coated microtitre plate wells was used to characterize the activity. All strains of P. intermedia tested, as well as those of the closely related species Prevotella nigrescens, showed a capacity to attach to the collagen film. Exponential-phase cultures of P. intermedia demonstrated a greater binding capacity than older cells. Attachment to the collagen film was inhibited by the presence of EDTA, type I and IV collagen, denatured collagen (gelatin), fibrinogen or fibronectin. Pretreatment of bacterial cells with heat (60 degrees C, 30 min) or proteinase K also inhibited the binding. The collagen-binding activity could be solubilized from the bacterial cell surface by incubation with Zwittergent 3-14, a zwitterionic detergent. The collagen-binding capacity of P. intermedia demonstrated in the present study represents a mechanism of colonization allowing these bacteria to attach to a tissue matrix.
Related Compounds
| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Molecular Formula | Articles |
|---|---|---|---|
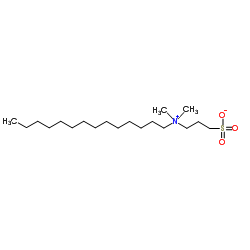 |
3-(N,N-Dimethylmyristylammonio)propanesulfonate
CAS:14933-09-6 |
C19H41NO3S |
|
Highly sensitive analysis of flavonoids by zwitterionic micr...
2014-09-05 [J. Chromatogr. A. 1358 , 277-84, (2014)] |
|
Metal complexes as artificial proteases in proteomics: a pal...
2011-05-01 [J. Inorg. Biochem. 105(5) , 675-83, (2011)] |
|
Electrospray mass spectra of three proprietary detergents.
2000-10-15 [Anal. Biochem. 285(2) , 205-10, (2000)] |
|
Electrokinetic injection across supported liquid membranes: ...
2012-09-01 [Electrophoresis 33 , 2695, (2012)] |
|
Highly selective extraction of spiralin from the Spiroplasma...
1985-12-01 [Biochimie 67(12) , 1251-6, (1985)] |