| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Articles |
|---|---|---|
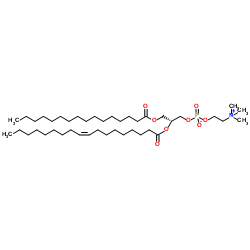 |
1-Palmitoyl-2-oleoyl-sn-glycero-3-PC
CAS:26853-31-6 |
|
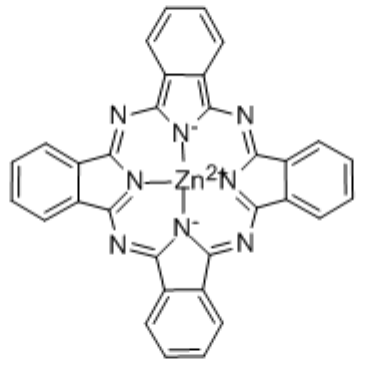 |
zinc phthalocyanine
CAS:14320-04-8 |