Rapid regulation of dopamine transporters by tyrosine kinases in rat neuronal preparations.
B R Hoover, C V Everett, A Sorkin, N R Zahniser
Index: J. Neurochem. 101(5) , 1258-71, (2007)
Full Text: HTML
Abstract
Termination of dopamine neurotransmission is primarily controlled by the plasma membrane-localized dopamine transporter. In this study, we investigated how this transporter is regulated by tyrosine kinases in neuronal preparations. In rat dorsal striatal synaptosomes, inhibition of tyrosine kinases by genistein or tyrphostin 23 resulted in a rapid (5-15 min), concentration-dependent decrease in [(3)H]dopamine uptake because of a reduction in maximal [(3)H]dopamine uptake velocity and dopamine transporter cell surface expression. The reduced transporter activity was associated with a decrease in phosphorylated p44/p42 mitogen-activated protein kinases. In primary rat mesencephalic neuronal cultures, the tyrosine kinase inhibitors similarly reduced [(3)H]dopamine uptake. When cultures were serum-deprived, acute activation of tyrosine kinase-coupled TrkB receptors by 100 ng/mL brain-derived neurotrophic factor significantly increased [(3)H]dopamine uptake; the effects were complex with increased maximal velocity but reduced affinity. The facilitatory effect of brain-derived neurotrophic factor on dopamine transporter activity depended on both the mitogen-activated protein kinase and phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase pathways. Taken together, our results suggest that striatal dopamine transporter function and cell surface expression is constitutively up-regulated by tyrosine kinase activation and that brain-derived neurotrophic factor can mediate this type of rapid regulation.
Related Compounds
| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Molecular Formula | Articles |
|---|---|---|---|
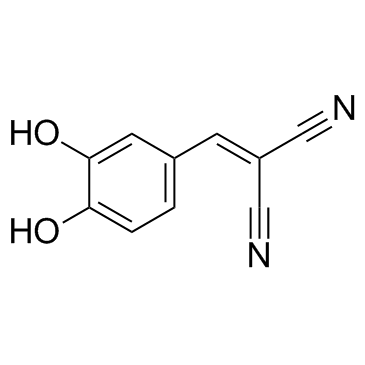 |
AG 18
CAS:118409-57-7 |
C10H6N2O2 |
|
Regulation of store-operated Ca2+ entry in pulmonary artery ...
2009-08-01 [Cell Calcium 46(2) , 99-106, (2009)] |
|
Spatio-temporal cellular dynamics of the Arabidopsis flagell...
2012-10-01 [Plant Cell 24(10) , 4205-19, (2012)] |
|
Swelling-activated K+ efflux and regulatory volume decrease ...
2006-01-01 [J. Membr. Biol. 214(1) , 33-41, (2006)] |
|
Role of kinases and G-proteins in the hyposmotic stimulation...
2006-10-01 [Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1758(10) , 1641-52, (2006)] |
|
Involvement of tyrosine kinase in the hyposmotic stimulation...
2008-06-01 [Pflugers Arch. 456(3) , 489-500, (2008)] |