Improving effect of ethyl eicosapentanoate on statin-induced rhabdomyolysis in Eisai hyperbilirubinemic rats.
Hiroyasu Naba, Chihaya Kakinuma, Shuhei Ohnishi, Takuo Ogihara
Index: Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 340(1) , 215-20, (2006)
Full Text: HTML
Abstract
The effect of ethyl eicosapentanoate (EPA-E) on statin-induced rhabdomyolysis was investigated by co-administration of EPA-E and pravastatin (PV), as a typical statin, to Eisai hyperbilirubinemic rats (EHBR). It was confirmed that the plasma PV concentration was not affected by simultaneous administration of EPA-E, and there was no cumulative increase of PV during prolonged co-administration of EPA-E and PV. Muscular degeneration was prominent (incidence 5/5; average grade 3.5 (range 2-4)) in EHBR treated with PV alone at 200 mg/kg/day for 14 days, but co-administration of EPA-E at doses of 100, 300, and 1000 mg/kg/day decreased the average grades to 1.4 (range 0.3-3.0), 0.5 (0.2-1.0), and 0.6 (0.0-1.7), respectively. Creatine phosphokinase (CPK) and myoglobin levels in plasma were well correlated with the grade of skeletal muscle degeneration. Thus, EPA-E appears to reduce the severity of statin-induced rhabdomyolysis.
Related Compounds
| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Molecular Formula | Articles |
|---|---|---|---|
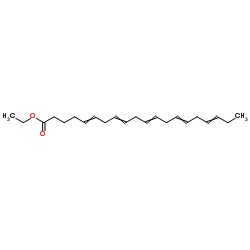 |
eicosapentaenoic acid ethyl ester
CAS:73310-10-8 |
C22H34O2 |
|
Protective effects of prescription n-3 fatty acids against i...
2011-07-01 [Food Funct. 2(7) , 386-94, (2011)] |
|
Usefulness of colon targeted DHA and EPA as novel diabetes m...
2008-12-08 [J. Control. Release 132(2) , 99-104, (2008)] |
|
Identification of inflammatory and proresolving lipid mediat...
2008-06-01 [Am. J. Hematol. 83(6) , 437-45, (2008)] |
|
Highly purified eicosapentaenoic acid prevents the progressi...
2009-04-01 [Prostaglandins Leukot. Essent. Fatty Acids 80(4) , 229-38, (2009)] |
|
Does eicosapentaenoic acid (EPA) inhibit cerebral vasospasm ...
2008-07-01 [Acta Neurol. Scand 118(1) , 54-9, (2008)] |