| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Articles |
|---|---|---|
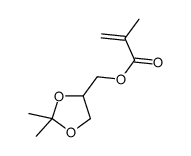 |
(2,2-dimethyl-1,3-dioxolan-4-yl)methyl methacrylate
CAS:7098-80-8 |
|
 |
Stearyl methacrylate
CAS:32360-05-7 |
|
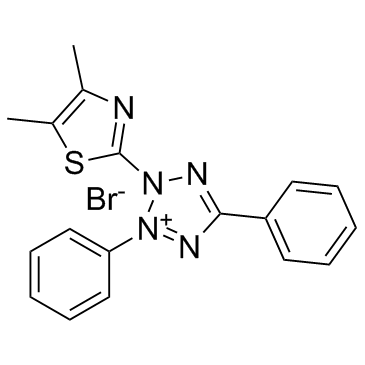 |
Thiazolyl Blue
CAS:298-93-1 |
|
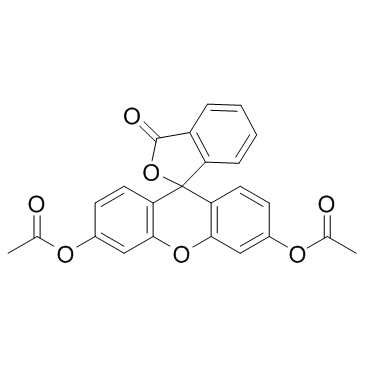 |
Fluorescein Diacetate
CAS:596-09-8 |