Interaction of acetylcholinesterase with the enantiomers of malaoxon and isomalathion.
C E Berkman, D A Quinn, C M Thompson
Index: Chem. Res. Toxicol. 6(5) , 724-30, (1993)
Full Text: HTML
Abstract
The biomolecular reaction constants (ki), dissociation constants (Kd), and phosphorylation constants (kp) were determined for the enantiomers of malaoxon against rat brain acetylcholinesterase, and for the stereoisomers of isomalathion against rat brain acetylcholinesterase and electric eel acetylcholinesterase. (R)-Malaoxon was an 8.6-fold more potent anti-cholinesterase than (S)-malaoxon. Isomalathion stereoisomers with the R configuration at carbon were 3-13-fold stronger inhibitors than those with the S configuration. The isomalathion stereoisomers with the R configuration at phosphorus were 4.3-8.8-fold stronger inhibitors of rat brain acetylcholinesterase, yet 3.4-5.8-fold weaker inhibitors of electric eel acetylcholinesterase, than the isomalathion stereoisomers with the S configuration at phosphorus. The rat brain acetylcholinesterase spontaneous (k0 = approximately 13.0 x 10(-3) min-1) and oxime-mediated (koxime) = 51.0 x 10(-3) min-1) reactivation rate constants following inhibition by isomalathion stereoisomers with the R configuration at phosphorus were comparable to spontaneous (11.3 x 10(-3) min-1) and oxime-mediated (50.2 x 10(-3) min-1) reactivation rates obtained for (S)-isoparathion methyl. These data support a common phosphorylation mechanism, namely, the displacement of the thiosuccinyl moiety from isomalathion stereoisomers with the R configuration at phosphorus, and displacement of the p-nitrophenoxy ligand from (S)-isoparathion methyl to form the same O,S-dimethyl phosphorothiolated enzyme. Rat brain acetylcholinesterase inhibited by the isomalathion stereoisomers with the S configuration at phosphorus were refractory to reactivation, suggesting an alternate mechanism of inhibition, i.e., the loss of the methylthio ligand. Several mechanisms are proposed to account for the subsequent nonreactivation.(ABSTRACT TRUNCATED AT 250 WORDS)
Related Compounds
| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Molecular Formula | Articles |
|---|---|---|---|
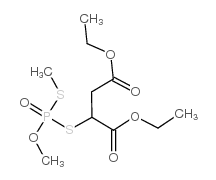 |
Isomalathion
CAS:3344-12-5 |
C10H19O6PS2 |
|
Probing the chiral separation mechanism and the absolute con...
2013-03-15 [J. Chromatogr. A. 1281 , 26-31, (2013)] |
|
Comparison of photocatalysis and photolysis of malathion, is...
2007-11-01 [Water Res. 41(19) , 4504-14, (2007)] |
|
An enzyme test for determining isomalathion impurities in wa...
1986-01-01 [Bull. World Health Organ. 64(3) , 397-401, (1986)] |
|
Toxicological properties of trialkyl phosphorothioate and di...
1983-01-01 [J. Environ. Sci. Health B 18(1) , 89-117, (1983)] |
|
Malathion detoxification by human hepatic carboxylesterases ...
2005-01-01 [J. Biochem. Mol. Toxicol. 19(6) , 406-14, (2005)] |