| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Articles |
|---|---|---|
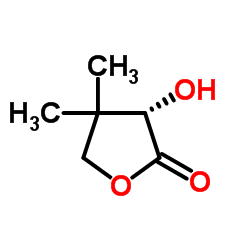 |
(S)-(+)-Pantolactone
CAS:5405-40-3 |
|
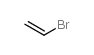 |
bromoethene
CAS:593-60-2 |
|
 |
DL-Pantolactone
CAS:79-50-5 |
|
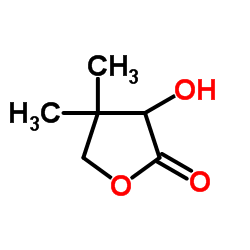 |
D-(-)-Pantolactone
CAS:599-04-2 |