Cryptosporidiosis: a rare and severe infection in a pediatric renal transplant recipient.
Yonca Acikgoz, Ozan Ozkaya, Kenan Bek, Gurkan Genc, Sema Gulnar Sensoy, Murat Hokelek
Index: Pediatr. Transplant. 16(4) , E115-9, (2012)
Full Text: HTML
Abstract
Cryptosporidium is an intracellular protozoan parasite that causes gastroenteritis in human. In immunocompromised individuals, cryptosporidium causes far more serious disease. There is no effective specific therapy for cryptosporidiosis, and spontaneous recovery is the rule in healthy individuals. However, immunocompromised patients need effective and prolonged therapy. Here, we present our clinical experience in a six-yr-old boy who underwent living-related donor renal transplantation and who was infected with Cryptosporidium spp. Our patient was successfully treated with antimicrobial agents consisting of spiramycin, nitazoxanide, and paromomycin. At the end of second week of therapy, his stool became negative for Cryptosporidium spp. antigen and spiramycin was discontinued. Nitazoxanide and paromomycin treatment was extended to four wk. With this case, we want to emphasize that cryptosporidiosis should be considered in the differential diagnosis of severe or persistent diarrhea in solid organ transplant recipients where rigorous antimicrobial therapy is needed.© 2011 John Wiley & Sons A/S.
Related Compounds
| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Molecular Formula | Articles |
|---|---|---|---|
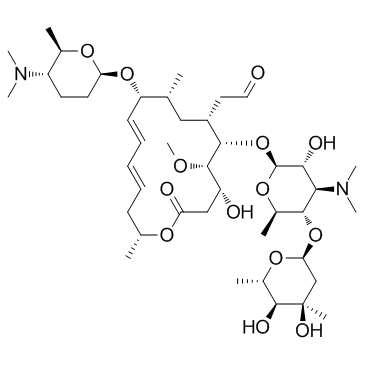 |
Spiramycin
CAS:8025-81-8 |
C43H74N2O14 |
|
Regulation of the biosynthesis of the macrolide antibiotic s...
2010-11-01 [J. Bacteriol. 192(21) , 5813-21, (2010)] |
|
A spicamycin derivative (KRN5500) provides neuropathic pain ...
2012-04-01 [J. Pain Symptom Manage. 43(4) , 679-93, (2012)] |
|
Influences of two antibiotic contaminants on the production,...
2012-01-01 [Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 77 , 79-87, (2012)] |
|
Significant reduction of brain cysts caused by Toxoplasma go...
2012-04-01 [Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 56(4) , 1762-8, (2012)] |
|
Antioxidant responses and degradation of two antibiotic cont...
2012-12-01 [Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 86 , 23-30, (2012)] |