Glutamatergic and GABAergic effects of fipronil on olfactory learning and memory in the honeybee.
Abdessalam Kacimi El Hassani, Julien Pierre Dupuis, Monique Gauthier, Catherine Armengaud
Index: Invert. Neurosci. 9(2) , 91-100, (2009)
Full Text: HTML
Abstract
We investigated here the role of transmissions mediated by GABA and glutamate-gated chloride channels (GluCls) in olfactory learning and memory in honeybees, both of these channels being a target for fipronil. To do so, we combined olfactory conditioning with injections of either the GABA- and glutamate-interfering fipronil alone, or in combination with the blocker of glutamate transporter L-trans-Pyrrolidine-2,4-Dicarboxylicacid (L-trans-PDC), or the GABA analog Trans-4-Aminocrotonic Acid (TACA). Our results show that a low dose of fipronil (0.1 ng/bee) impaired olfactory memory, while a higher dose (0.5 ng/bee) had no effect. The detrimental effect induced by the low dose of fipronil was rescued by the coinjection of L-trans-PDC but was rather increased by the coinjection of TACA. Moreover, using whole-cell patch-clamp recordings, we observed that L-trans-PDC reduced glutamate-induced chloride currents in antennal lobe cells. We interpret these results as reflecting the involvement of both GluCl and GABA receptors in the impairment of olfactory memory induced by fipronil.
Related Compounds
| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Molecular Formula | Articles |
|---|---|---|---|
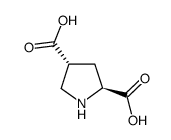 |
trans-4-Carboxy-L-proline
CAS:64769-66-0 |
C6H9NO4 |
|
Evidence for a role of GABA- and glutamate-gated chloride ch...
2012-11-01 [Pharmacol. Biochem. Behav. 103(1) , 69-75, (2012)] |
|
Substituted pyrrolidine-2,4-dicarboxylic acid amides as pote...
2006-06-15 [Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 16(12) , 3268-72, (2006)] |
|
The effects of local perfusion of DAMGO on extracellular GAB...
2008-02-01 [J. Neurochem. 104(3) , 806-17, (2008)] |
|
Effects of theanine, r-glutamylethylamide, on neurotransmitt...
2005-08-01 [Nutr. Neurosci. 8(4) , 219-26, (2005)] |
|
Dissociation between hippocampal neuronal loss, astroglial a...
2006-12-01 [Neurochem. Int. 49(7) , 691-7, (2006)] |