Inhibition of nitric oxide synthase aggravates cisplatin-induced nephrotoxicity: effect of 2-amino-4-methylpyridine.
Sherif Y Saad, Tawfeeg A O Najjar, Mohammed H Daba, Ammar C Al-Rikabi
Index: Chemotherapy 48(6) , 309-15, (2002)
Full Text: HTML
Abstract
Nitric oxide (NO) has been shown to play a role in maintaining normal renal function. However, the role of NO in cisplatin (CDDP)-induced nephrotoxicity is still unclear. The aim of the present work was to examine the effect of the NO synthase (NOS) inhibitor, 2-amino-4-methylpyridine, on the severity of CDDP-induced nephrotoxicity.Male Wistar rats were divided into six groups. Three control groups received plain drinking water or water containing 1.5% L-arginine. One of the two groups receiving plain water was treated with an intraperitoneal injection of 2-amino-4-methylpyridine (1 mg/kg in normal saline), and the other two control groups were injected intraperitoneally with normal saline. Another three groups were treated in the same manner and injected with CDDP (6 mg/kg, i.p.). CDDP was injected 1 h after 2-amino-4-methylpyridine treatment. Rats were sacrificed 7 days after CDDP treatment, and serum as well as kidneys were isolated and analysed.CDDP-treated rats showed increases in the kidney weight as a percentage of the total body weight and serum creatinine and urea levels and decreases in serum albumin and calcium levels. Also, CDDP treatment induced reductions in the kidney total nitrate/nitrite (NO(x)), reduced glutathione (GSH) and glutathione peroxidase activity (GSH-Px) levels and an increase in the kidney malondialdehyde (MDA) production level. In contrast, 2-amino-4-methylpyridine treatment 1 h prior to CDDP injection induced marked exacerbation of CDDP-induced nephrotoxicity, as manifested by severe aggravation of the indices of nephrotoxicity. Also, 2-amino-4-methylpyridine plus CDDP-treated rats showed exaggeration of the reduction in the kidney total NO(x) content and GSH-Px activity and elevation of the kidney platinum accumulation level with normalization of the kidney MDA production level and rebound in the kidney GSH content. Histopathologically, CDDP-treated rats showed marked interstitial nephritis, tubular atrophy and tubular necrosis. However, treatment with 2-amino-4-methylpyridine 1 h prior to CDDP injection revealed marked exacerbation of CDDP-induced histopathological changes.The present findings suggest that NO plays a role in CDDP-induced nephrotoxicity. Administration of 2-amino-4-methylpyridine, an NOS inhibitor, exacerbates CDDP-induced nephrotoxicity.Copyright 2002 S. Karger AG, Basel
Related Compounds
| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Molecular Formula | Articles |
|---|---|---|---|
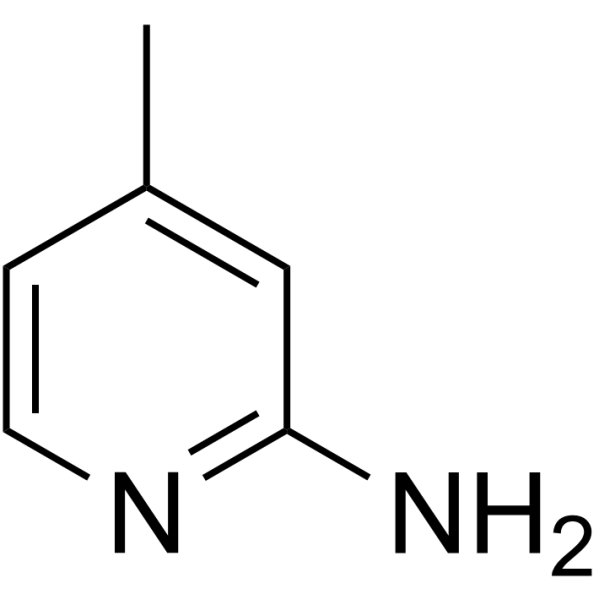 |
Aminopicoline
CAS:695-34-1 |
C6H8N2 |
|
Guide to Receptors and Channels (GRAC), 4th Edition.
2009-11-01 [Br. J. Pharmacol. 158 Suppl 1 , S1-254, (2009)] |
|
Synthesis and evaluation of pyrido[1,2-a]pyrimidines as inhi...
2009-07-01 [Eur. J. Med. Chem. 44 , 2877-87, (2009)] |
|
Actions of 4-methyl-2-aminopyridine on neuromuscular transmi...
1981-03-05 [Eur. J. Pharmacol. 70(1) , 53-7, (1981)] |
|
On the mechanism of action of 2-amino-4-methylpyridine, a mo...
1980-10-01 [Arch. Int. Pharmacodyn. Ther. 247(2) , 275-82, (1980)] |
|
Differential activity of NO synthase inhibitors as chemoprev...
2002-01-01 [Neoplasia 4(4) , 332-6, (2002)] |