| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Articles |
|---|---|---|
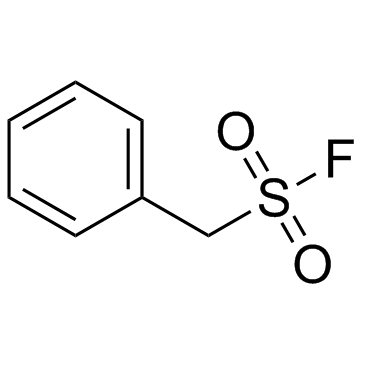 |
PMSF
CAS:329-98-6 |
|
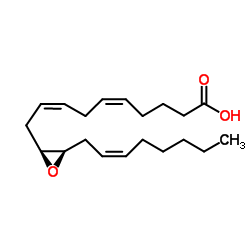 |
(11S,12R)-EET
CAS:123931-40-8 |