| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Articles |
|---|---|---|
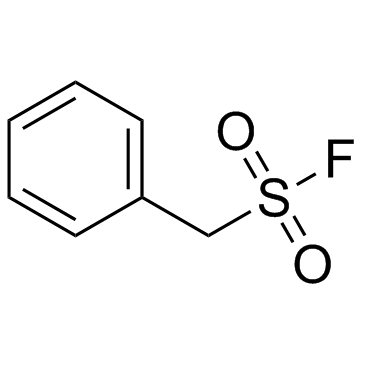 |
PMSF
CAS:329-98-6 |
|
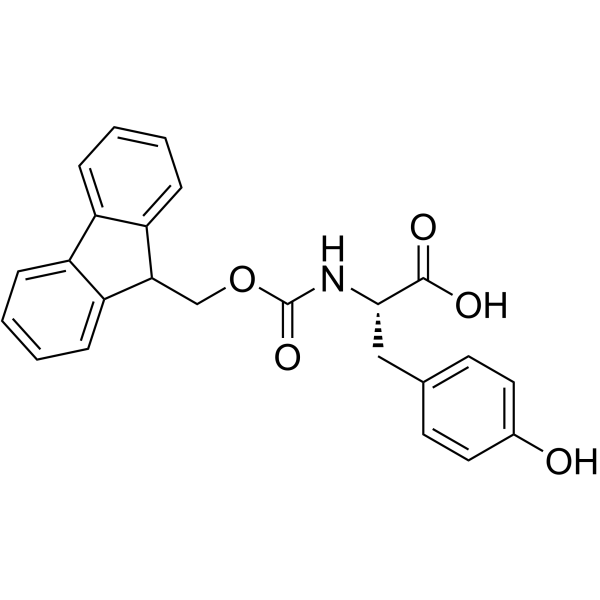 |
Fmoc-Tyr-OH
CAS:92954-90-0 |
|
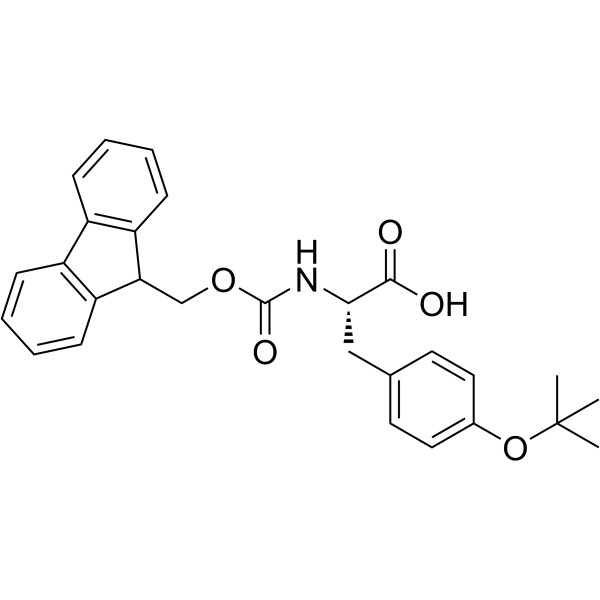 |
Fmoc-Tyr(tBu)-OH
CAS:71989-38-3 |
|
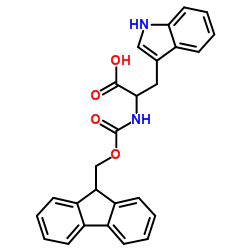 |
Fmoc-Trp-OH
CAS:35737-15-6 |
|
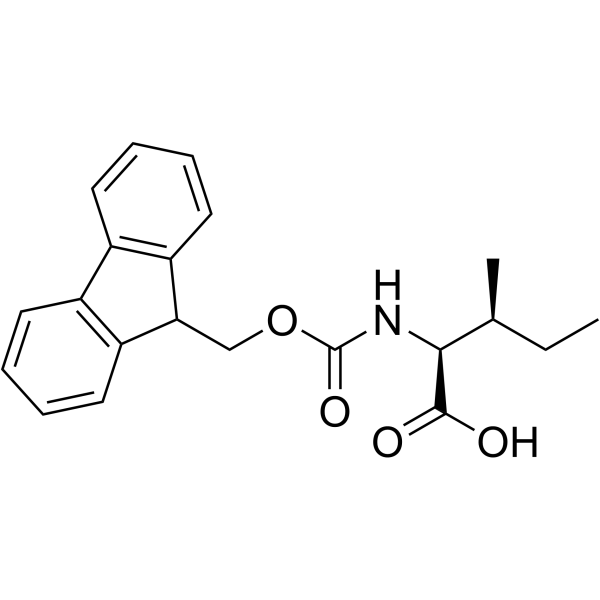 |
Fmoc-Ile-OH
CAS:71989-23-6 |
|
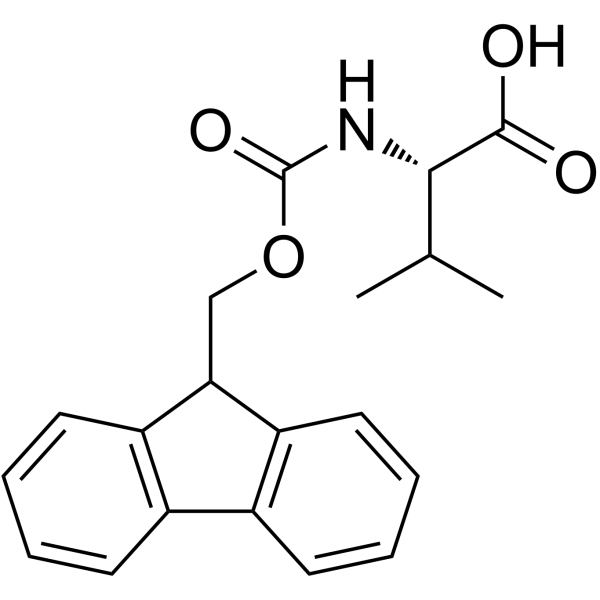 |
Fmoc-Val-OH
CAS:68858-20-8 |
|
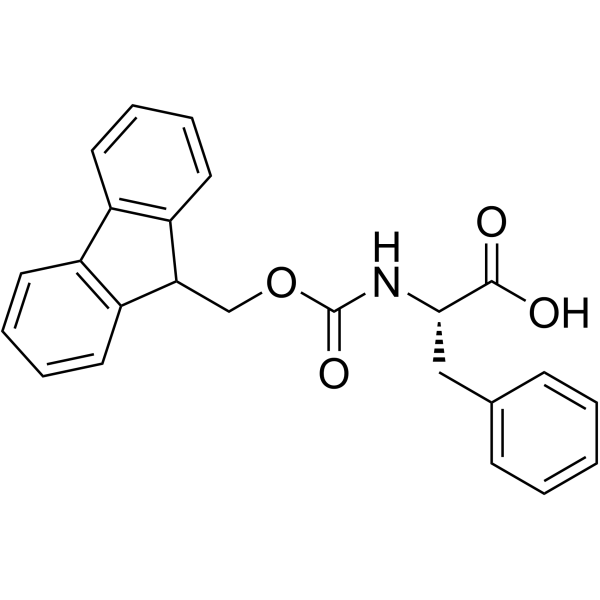 |
FMOC-L-Phenylalanine
CAS:35661-40-6 |