| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Articles |
|---|---|---|
 |
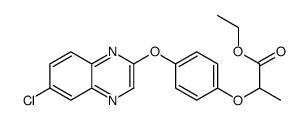
quizalofop-P-ethyl
CAS:100646-51-3 |
|
 |
quizalofop-ethyl
CAS:76578-14-8 |
|
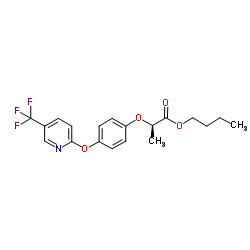 |
fluazifop-P-butyl
CAS:79241-46-6 |
|
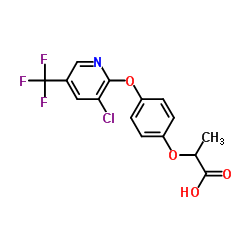 |
haloxyfop
CAS:69806-34-4 |
|
![Propanoic acid,2-[4-[[5-(trifluoromethyl)-2-pyridinyl]oxy]phenoxy]-, butyl ester Structure](https://image.chemsrc.com/caspic/312/69806-50-4.png) |
Propanoic acid,2-[4-[[5-(trifluoromethyl)-2-pyridinyl]oxy]phenoxy]-, butyl ester
CAS:69806-50-4 |