| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Articles |
|---|---|---|
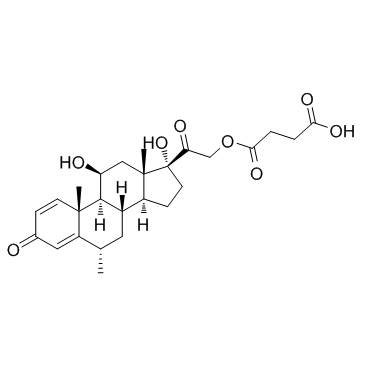 |
Methylprednisolone succinate
CAS:2921-57-5 |
|
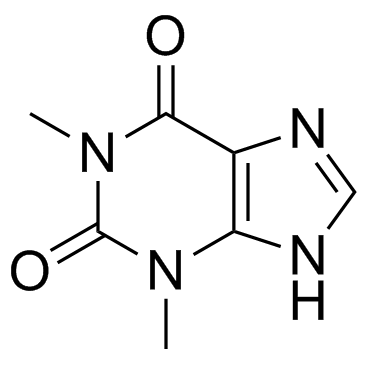 |
Theophylline
CAS:58-55-9 |
|
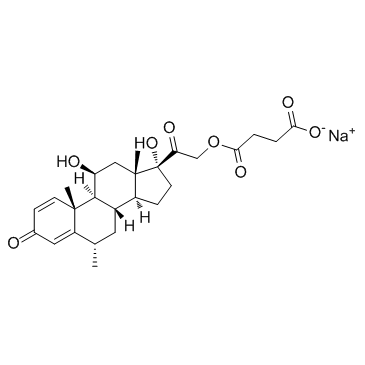 |
6alpha-Methylprednisolone sodium succinate
CAS:2375-03-3 |