Anaerobic biodegradation of hexazinone in four sediments.
Huili Wang, Shuxia Xu, Chengxia Tan, Xuedong Wang
Index: J. Hazard. Mater. 164(2-3) , 806-11, (2009)
Full Text: HTML
Abstract
Anaerobic biodegradation of hexazinone was investigated in four sediments (L1, L2, Y1 and Y2). Results showed that the L2 sediment had the highest biodegradation potential among four sediments. However, the Y1 and Y2 sediments had no capacity to biodegrade hexazinone. Sediments with rich total organic carbon, long-term contamination history by hexazinone and neutral pH may have a high biodegradation potential because the former two factors can induce the growth of microorganisms responsible for biodegradation and the third factor can offer suitable conditions for biodegradation. The addition of sulfate or nitrate as electron acceptors enhanced hexazinone degradation. As expected, the addition of electron donors (lactate, acetate or pyruvate) substantially inhibited the degradation. In natural environmental conditions, the effect of intermediate A [3-(4-hydroxycyclohexyl)-6-(dimethylamino)-1-methyl-1,3,5-triazine-2,4(1H, 3H)dione] on anaerobic hexazinone degradation was negligible because of its low level.
Related Compounds
| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Molecular Formula | Articles |
|---|---|---|---|
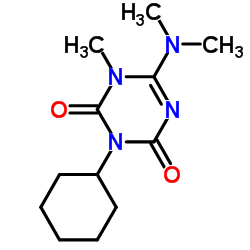 |
Hexazinone
CAS:51235-04-2 |
C12H20N4O2 |
|
The interaction between natural organic matter in raw waters...
2013-01-01 [Water Sci. Technol. 67(11) , 2428-36, (2013)] |
|
Dissipation of four forest-use herbicides at high latitudes.
2008-10-01 [Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. Int. 15(7) , 573-83, (2008)] |
|
Comparison between the short-term and the long-term toxicity...
2009-01-01 [Water Res. 43(6) , 1731-9, (2009)] |
|
Combined photobacterium toxicity of herbicide mixtures conta...
2009-04-01 [Chemosphere 75(3) , 381-8, (2009)] |
|
Impacts of stage-specific acute pesticide exposure on predic...
2010-07-01 [Aquat. Toxicol. 98(3) , 265-74, (2010)] |