| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Articles |
|---|---|---|
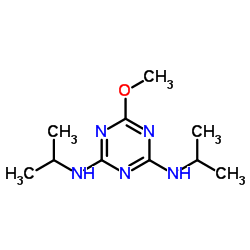 |
Prometon
CAS:1610-18-0 |
|
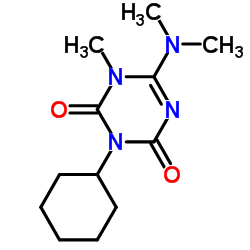 |
Hexazinone
CAS:51235-04-2 |
|
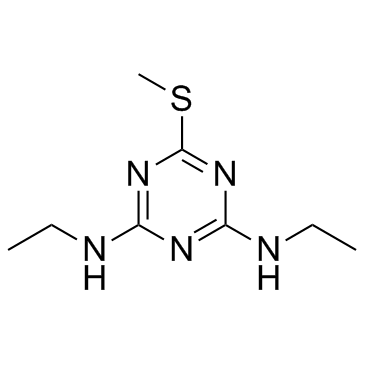 |
Simetryn
CAS:1014-70-6 |
|
 |
semeron
CAS:1014-69-3 |