Demethylwedelolactone derivatives inhibit invasive growth in vitro and lung metastasis of MDA-MB-231 breast cancer cells in nude mice.
Yean-Jang Lee, Wea-Lung Lin, Nai-Fang Chen, Shien-Kai Chuang, Tsui-Hwa Tseng
Index: Eur. J. Med. Chem. 56 , 361-7, (2012)
Full Text: HTML
Abstract
The anticancer properties of demethylwedelolactone (DWEL) and wedelolactone (WEL), which are naturally occurring coumestans, have not been well characterized. In this study, we investigated the anti-invasive effects of synthetic WEL and DWEL on human MDA-MB-231 breast cancer cells. We found that WEL and DWEL inhibited the anchorage-independent growth and also suppressed cell motility and cell invasion of MDA-MB-231 cells. In addition, WEL and DWEL reduced the activity and expression of matrix metalloproteinases (MMPs) involved in blocking the IκB-α/NFκB and MEK/ERK signaling pathways in MDA-MB-231 cells. Furthermore, DWEL suppressed the metastasis and lung colonization of the tumor cells in the nude mice. Altogether, these data suggest that DWEL derivatives exert anti-invasive growth effect on breast cancer cells.Copyright © 2012 Elsevier Masson SAS. All rights reserved.
Related Compounds
| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Molecular Formula | Articles |
|---|---|---|---|
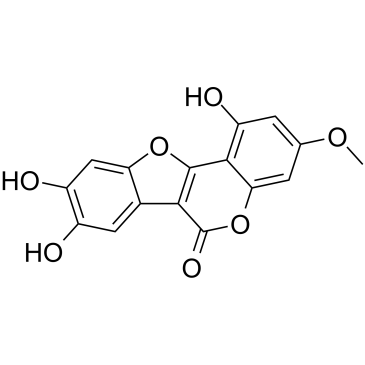 |
wedelolactone
CAS:524-12-9 |
C16H10O7 |
|
Understanding the mechanisms controlling Leishmania amazonen...
2014-08-15 [J. Infect. Dis. 210(4) , 656-66, (2014)] |
|
CYLD is a crucial negative regulator of innate immune respon...
2013-11-19 [Cell. Microbiol. 10(11) , 2247-56, (2008)] |
|
Wedelolactone, a medicinal plant-derived coumestan, induces ...
2012-12-01 [Int. J. Oncol. 41(6) , 2191-9, (2012)] |
|
Anti-inflammatory gallic Acid and wedelolactone are G protei...
2012-01-01 [Pharmacology 89(3-4) , 211-9, (2012)] |
|
High glucose-induced IKK-Hsp-90 interaction contributes to e...
2009-01-01 [Am. J. Physiol. Cell Physiol. 296(1) , C182-92, (2009)] |