Simulation of in situ subsurface biodegradation of polychlorophenols in air-lift percolators.
J H Langwaldt, M K Männistö, R Wichmann, J A Puhakka
Index: Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 49(6) , 663-8, (1998)
Full Text: HTML
Abstract
Air-lift percolator experiments simulated in situ subsurface degradation of 2,4,6-trichlorophenol, 2,3,4,6-tetrachlorophenol and pentachlorophenol, in mixtures and individually, by indigenous microorganisms from a chlorophenol-contaminated aquifer. Inoculation with a chlorophenol(CP)-degrading gram-positive isolate from the CP-contaminated groundwater did not significantly increase CP degradation rates. Feed concentrations of up to 55 mg CP l-1 were degraded. Stable CP degradation was maintained for over 6 months. CP degradation rates up to 54.3 mg l-1 day-1 and effluent concentrations below 40 micrograms CP l-1 were achieved. CP were mineralized as shown by CP reduction, dissolved organic carbon removal and release of inorganic chloride.
Related Compounds
| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Molecular Formula | Articles |
|---|---|---|---|
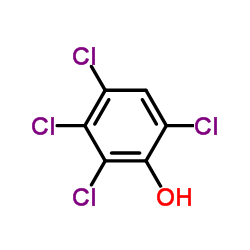 |
2,3,4,6-TETRACHLOROPHENOL
CAS:58-90-2 |
C6H2Cl4O |
|
PCDD/F formation from chlorophenols by lignin and manganese ...
2014-09-01 [Chemosphere 110 , 129-35, (2014)] |
|
Comparison of stir bar sorptive extraction and solid-phase m...
2008-05-15 [Talanta 75(3) , 753-9, (2008)] |
|
In situ polychlorophenol bioremediation potential of the ind...
2001-07-01 [Water Res. 35(10) , 2496-504, (2001)] |
|
Chemical kinetic modelling of PCDD formation from chlorophen...
2000-09-01 [Chemosphere 41(6) , 943-51, (2000)] |
|
Metabolism of Halophenols by 2,4,5-trichlorophenoxyacetic ac...
1983-11-01 [Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 46(5) , 1176-81, (1983)] |