Acrosin inhibitor, 4'-acetamidophenyl 4-guanidinobenzoate, an experimental vaginal contraceptive with anti-HIV activity.
A S Bourinbaiar, S Lee-Huang
Index: Contraception 51(5) , 319-22, (1995)
Full Text: HTML
Abstract
Serine proteases are involved in a wide variety of seemingly unrelated physiological functions including capacitation of the spermatozoa and potentiation of human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) infection. The experimental vaginal contraceptives derived from 4-guanidinobenzoic acid act through inhibition of acrosin--a serine protease from the sperm. The serial ten-fold dilutions of 4'-acetamidophenyl 4-guanidinobenzoate (AGB) were tested in vitro for the effect against HIV infection by assaying the suppression of de novo p24 synthesis in virus-inoculated MT-4 T lymphocytes. The results reveal that complete inhibition of HIV occurred at 100 micrograms/ml--a dose corresponding to previously reported concentrations responsible for preventing fertilization in rabbits. These findings suggest that serine protease inhibitors and in particular the guanidinobenzoates, reported to be up to 100-fold more potent and less irritating than nonoxynol-9, can be potentially operative against sexual transmission of HIV.
Related Compounds
| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Molecular Formula | Articles |
|---|---|---|---|
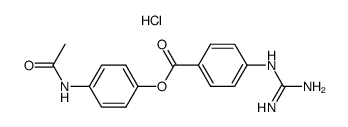 |
4'-ACETAMIDOPHENYL 4-GUANIDINOBENZOATE HYDROCHLORIDE
CAS:79119-49-6 |
C16H17ClN4O3 |
|
Inhibition of a tumour protease with 3,4-dichloroisocoumarin...
1994-01-01 [J. Enzym. Inhib. 8(3) , 213-21, (1994)] |
|
Synthesis and inhibition of human acrosin and trypsin and ac...
1986-04-01 [J. Med. Chem. 29 , 514, (1986)] |
|
Trypsin inhibitors prevent the progesterone-initiated increa...
1991-06-01 [J. Exp. Zool. 258(3) , 384-93, (1991)] |
|
Inhibition of the human sperm acrosome reaction by proteinas...
1989-08-01 [Gamete Res. 23(4) , 387-97, (1989)] |
|
Characterization of acrosin-like activity of lake sturgeon (...
1996-09-01 [Mol. Reprod. Dev. 45(1) , 72-7, (1996)] |