Cloxacillin as an antibiotic lock solution for prevention of catheter-associated infection.
Mozhgan Davanipur, Maryam Pakfetrat, Jamishid Roozbeh
Index: Iran. J. Kidney Dis. 5(5) , 328-31, (2011)
Full Text: HTML
Abstract
Catheter-related infection is associated with increased all-cause mortality and morbidity in hemodialysis patients. This study aimed to evaluate an antimicrobial lock solution (cloxacillin and heparin) in temporary noncuffed double-lumen catheters for long-term intermittent hemodialysis as a method of preventing catheter-related infection.Patients on hemodialysis with noncuffed temporary double lumen catheter were randomly divided into 2 groups. Fifty patients received a solution containing cloxacillin, 100 mg/mL, plus heparin, 1000 IU/mL as a 2.5-mL solution instilled in each of catheter lumens after dialysis session. Another 50 patients received only heparin. They were allowed to dwell until the next session of dialysis.One catheter-related bacteremia was observed in the antibiotic group whereas catheter-related bacteremia was observed in 8 of those who received heparin only. The rate of catheter-related bacteremia episodes were 0.5 per 1000 catheter-days in the antibiotic group versus 7.8 per 1000 catheter-days in the control group (P = .02).In the present study, application of cloxacillin as antibiotic lock solution for dialysis catheters resulted in a considerable reduction in catheter-related bacteremia rate.
Related Compounds
| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Molecular Formula | Articles |
|---|---|---|---|
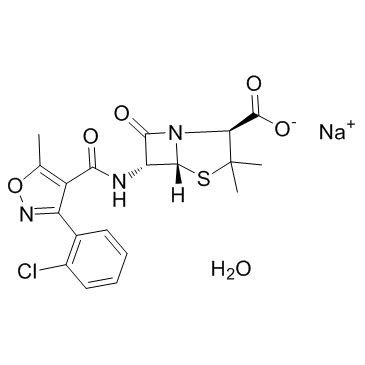 |
Cloxacillin Sodium
CAS:7081-44-9 |
C19H19ClN3NaO6S |
|
Combined disc methods for the detection of KPC- and/or VIM-p...
2013-09-01 [Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 19(9) , E412-5, (2013)] |
|
Intravenous infusion of electrolyte solution changes pharmac...
2014-10-01 [J. Vet. Pharmacol. Ther. 37(5) , 445-50, (2014)] |
|
Opalescent grouped vesicles over the face: an important indi...
2012-01-01 [Pediatr. Dermatol. 29(2) , 230-2, (2012)] |
|
A probable clinically significant interaction between warfar...
2013-03-01 [Eur. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 69(3) , 721-4, (2013)] |
|
Diagnostic utility of combination of inducer and inhibitor b...
2011-10-01 [J. Microbiol. Methods 87(1) , 116-8, (2011)] |