The mechanism of the reduction of [AnO2]2+ (An = U, Np, Pu) in aqueous solution, and by Fe(II) containing proteins and mineral surfaces, probed by DFT calculations.
Mahesh Sundararajan, Rajeev S Assary, Ian H Hillier, David J Vaughan
Index: Dalton Trans. 40(42) , 11156-63, (2011)
Full Text: HTML
Abstract
The fate of actinyl species in the environment is closely linked to oxidation state, since the reduction of An(VI) to An(IV) greatly decreases their mobility due to the precipitation of the relatively insoluble An(IV) species. Here we study the mechanism of the reduction of [AnO(2)](2+) (An = U, Np, Pu) both in aqueous solution and by Fe(II) containing proteins and mineral surfaces, using density functional theory calculations. We find a disproportionation mechanism involving a An(V)-An(V) cation-cation complex, and we have investigated how these complexes are formed in the different environments. We find that the behaviour of U and Pu complexes are similar, but the reduction of Np(V) to Np(IV) would seems to be more difficult, in line with the experimental finding that Np(V) is generally more stable than U(V) or Pu(V). Although the models we have used are somewhat idealised, our calculations suggest that there are strong similarities between the biotic and abiotic reduction pathways.
Related Compounds
| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Molecular Formula | Articles |
|---|---|---|---|
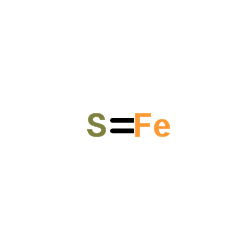 |
Ferrous sulfide
CAS:1317-37-9 |
FeS |
|
Enhanced reductive dechlorination of tetrachloroethene durin...
2012-10-15 [J. Hazard. Mater. 235-236 , 359-66, (2012)] |
|
Black stain - a review.
2011-01-01 [Oral Health Prev. Dent. 9(1) , 37-45, (2011)] |
|
Selenide retention by mackinawite.
2012-09-18 [Environ. Sci. Technol. 46(18) , 10004-11, (2012)] |
|
FeS/S/FeS(2) redox system and its oxidoreductase-like chemis...
2011-06-01 [Astrobiology 11(5) , 471-6, (2011)] |
|
Removal of highly elevated nitrate from drinking water by pH...
2011-11-01 [Bioresour. Technol. 102(21) , 10154-7, (2011)] |