| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Articles |
|---|---|---|
 |
HEPES
CAS:7365-45-9 |
|
 |
L-Glutamine
CAS:56-85-9 |
|
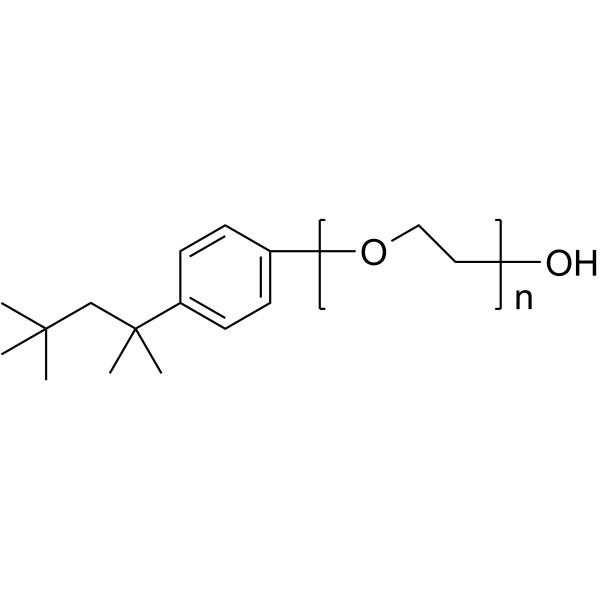 |
Triton X-100
CAS:9002-93-1 |
|
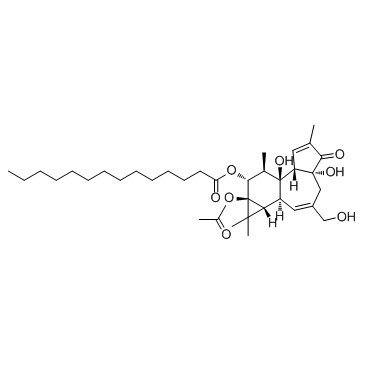 |
12-O-tetradecanoylphorbol-13-acetate
CAS:16561-29-8 |
|
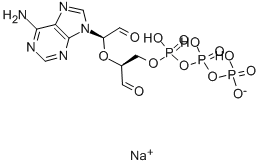 |
ADENOSINE 5'-TRIPHOSPHATE,PERIODATE OXIDIZED SODIUM SALT
CAS:71997-40-5 |