Metabolic fate of 14C-camostat mesylate in man, rat and dog after intravenous administration.
I Midgley, A J Hood, P Proctor, L F Chasseaud, S R Irons, K N Cheng, C J Brindley, R Bonn
Index: Xenobiotica 24(1) , 79-92, (1994)
Full Text: HTML
Abstract
1. The metabolic fate of N,N-dimethylcarbamoylmethyl 4-(4-guanidino[14C]benzoyloxy)phenylacetate methanesulphonate (14C-camostat mesylate) was investigated after i.v. administration to man (12-h infusion), and to rat and dog (bolus injection). 2. Renal excretion (mainly in 24 h) accounted for at least 80% dose in all three species, and the only two important metabolites were identified as 4-(4-guanidinobenzoyloxy)phenylacetic acid (GBPA) and 4-guanidinobenzoic acid (GBA). 3. Parent drug was not detected in human plasma either during or after infusion of 14C-camostat mesylate owing to rapid hydrolysis of the side-chain ester group (t1/2 < 1 min). Steady-state levels of both GBPA and GBA in plasma were apparently attained by the end of the infusion period. Mean terminal half-life, systemic clearance and apparent volume of distribution at steady-state of GBPA in man were 1.0 h, 6.4 ml/min per kg and 0.38 l/kg, respectively, and the corresponding values for GBA were 2.4 h, 4.7 ml/min per kg and 1.01/kg respectively. 4. Radioactivity was rapidly distributed to most tissues after bolus i.v. doses of 14C-camostat mesylate to rats and dogs, with highest levels being associated with the liver and kidney, the two main organs of drug elimination. Concentrations in the pancreas, a possible site for drug action, were generally lower than those in plasma.
Related Compounds
| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Molecular Formula | Articles |
|---|---|---|---|
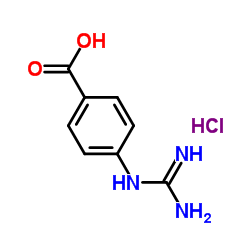 |
N-(4-Carboxyphenyl)guanidine hydrochloride
CAS:42823-46-1 |
C8H10ClN3O2 |
|
The specificity of murine polyclonal and monoclonal antibodi...
1987-07-01 [Clin. Exp. Immunol. 69(1) , 157-65, (1987)] |
|
Evidence for an enzyme which cleaves the guanidinobenzoate m...
1983-02-01 [Eur. J. Biochem. 130(2) , 335-9, (1983)] |
|
Inhibition of prostasin secretion by serine protease inhibit...
2003-01-01 [J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 14(1) , 11-6, (2003)] |
|
Mechanisms of the hyperkalaemia caused by nafamostat mesilat...
1994-01-01 [Br. J. Pharmacol. 111(1) , 173-8, (1994)] |
|
Elimination of the low-molecular weight proteinase inhibitor...
1987-01-01 [Res. Exp. Med. (Berl.) 187(6) , 401-6, (1987)] |