Elimination of the low-molecular weight proteinase inhibitor camostate (FOY 305) and its degradation products by the rat liver.
K Beckh, B Göke, R Müller, R Arnold
Index: Res. Exp. Med. (Berl.) 187(6) , 401-6, (1987)
Full Text: HTML
Abstract
The elimination of the low molecular weight proteinase inhibitor camostate (FOY 305) was studied in rats after oral administration and in the the situ perfused rat liver. After feeding of camostate (400 mg/kg b.w.) only the metabolites (FOY 251, GBA) were detected in blood samples withdrawn from the portal and hepatic vein. This indicated a rapid degradation of FOY 305 after absorption from the gut lumen. The hepatic extraction of the anti-proteolytic active metabolite FOY 251 during a single liver passage was 23%. It remained almost constant over the period of 120 min. In the perfused rat liver, FOY 305 was given in concentrations comparable to the in vivo studies. It was eliminated by 20%. In these experiments, the compound was metabolized to FOY 251 and in minor amounts to guanidino-benzoate (GBA), the latter being an anti-proteolytic ineffective degradation product. In conclusion, a low hepatic extraction of FOY 305 led to pharmacologically effective concentrations of the active metabolite FOY 251 in the circulation after oral ingestion of the proteinase inhibitor.
Related Compounds
| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Molecular Formula | Articles |
|---|---|---|---|
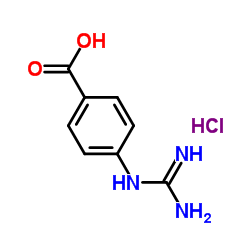 |
N-(4-Carboxyphenyl)guanidine hydrochloride
CAS:42823-46-1 |
C8H10ClN3O2 |
|
The specificity of murine polyclonal and monoclonal antibodi...
1987-07-01 [Clin. Exp. Immunol. 69(1) , 157-65, (1987)] |
|
Evidence for an enzyme which cleaves the guanidinobenzoate m...
1983-02-01 [Eur. J. Biochem. 130(2) , 335-9, (1983)] |
|
Inhibition of prostasin secretion by serine protease inhibit...
2003-01-01 [J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 14(1) , 11-6, (2003)] |
|
Mechanisms of the hyperkalaemia caused by nafamostat mesilat...
1994-01-01 [Br. J. Pharmacol. 111(1) , 173-8, (1994)] |
|
Kinetics and mechanism for the conformational transition in ...
1979-11-01 [Biophys. Chem. 10(3-4) , 253-60, (1979)] |