| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Articles |
|---|---|---|
 |
Triazolam
CAS:28911-01-5 |
|
 |
Zaleplon
CAS:151319-34-5 |
|
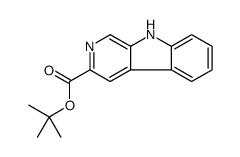 |
tert-butyl beta-carboline-3-carboxylate
CAS:93835-05-3 |