Journal of Organic Chemistry
2002-06-28
Ginkgolides: selective acetylations, translactonization, and biological evaluation.
Stanislav Jaracz, Kristian Strømgaard, Koji Nakanishi
Index: J. Org. Chem. 67(13) , 4623-6, (2002)
Full Text: HTML
Abstract
Protocols for selective acetylation of the hydroxyl groups of ginkgolide C have been developed. These acetylations have given rise to various ginkgolide C acetates and iso-ginkgolide C acetates, the latter having a rearranged skeleton resulting from translactonization. These acetyl derivatives, as well as ginkgolides A and B acetates have been investigated for their ability to bind to a cloned platelet-activating factor (PAF) receptor.
Related Compounds
| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Molecular Formula | Articles |
|---|---|---|---|
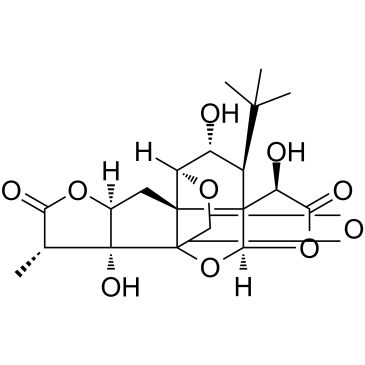 |
Ginkgolide J
CAS:107438-79-9 |
C20H24O10 |
Related Articles:
More...
|
Complete 1H NMR spectral analysis of ten chemical markers of...
2012-08-01 [Magn. Reson. Chem. 50(8) , 569-75, (2012)] |
|
Rapid analysis of terpene lactones in extract of Ginkgo bilo...
2000-09-01 [Se Pu 18(5) , 394-7, (2000)] |
|
Protection against beta-amyloid induced abnormal synaptic fu...
2009-02-01 [Neurobiol. Aging 30(2) , 257-65, (2009)] |
|
Isolation of ginkgolides A, B, C, J and bilobalide from G. b...
2004-11-01 [Phytochemistry 65(21) , 2897-902, (2004)] |
|
A method for extraction and quantification of Ginkgo terpene...
2004-08-01 [Anal. Chem. 76(15) , 4332-6, (2004)] |