Protection against beta-amyloid induced abnormal synaptic function and cell death by Ginkgolide J.
Ottavio Vitolo, Bing Gong, Zixuan Cao, Hideki Ishii, Stanislav Jaracz, Koji Nakanishi, Ottavio Arancio, Sergei V Dzyuba, Roger Lefort, Michael Shelanski
Index: Neurobiol. Aging 30(2) , 257-65, (2009)
Full Text: HTML
Abstract
A new Ginkgo biloba extract P8A (TTL), 70% enriched with terpene trilactones, prevents A beta(1-42) induced inhibition of long-term potentiation in the CA1 region of mouse hippocampal slices. This neuroprotective effect is attributed in large part to ginkgolide J that completely replicates the effect of the extract. Ginkgolide J is also capable of inhibiting cell death of rodent hippocampal neurons caused by A beta(1-42). This beneficial and multi-faceted mode of action of the ginkgolide makes it a new and promising lead in designing therapies against Alzheimer's disease.
Related Compounds
| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Molecular Formula | Articles |
|---|---|---|---|
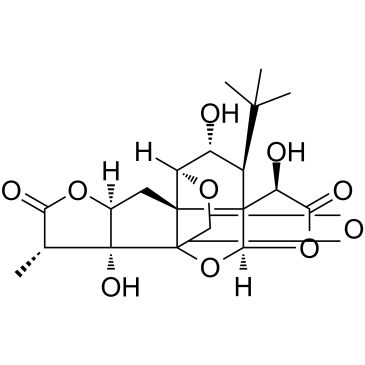 |
Ginkgolide J
CAS:107438-79-9 |
C20H24O10 |
|
Complete 1H NMR spectral analysis of ten chemical markers of...
2012-08-01 [Magn. Reson. Chem. 50(8) , 569-75, (2012)] |
|
Rapid analysis of terpene lactones in extract of Ginkgo bilo...
2000-09-01 [Se Pu 18(5) , 394-7, (2000)] |
|
Isolation of ginkgolides A, B, C, J and bilobalide from G. b...
2004-11-01 [Phytochemistry 65(21) , 2897-902, (2004)] |
|
A method for extraction and quantification of Ginkgo terpene...
2004-08-01 [Anal. Chem. 76(15) , 4332-6, (2004)] |
|
Ginkgolides: selective acetylations, translactonization, and...
2002-06-28 [J. Org. Chem. 67(13) , 4623-6, (2002)] |