Selective cleavage of proenkephalin-derived peptides (less than 23,300 daltons) by plasma kallikrein.
K M Metters, J Rossier, J Paquin, M Chrétien, N G Seidah
Index: J. Biol. Chem. 263(25) , 12543-53, (1988)
Full Text: HTML
Abstract
The ability of human plasma kallikrein to hydrolyze several proenkephalin-derived peptides has been studied, including the synthetic peptides BAM 12P and peptides E, F, and B as well as synenkephalin-containing peptides (8.6, 18.2, and 23.3 kDa) purified from bovine adrenal medulla chromaffin granules. All the identified cleavages occurred either COOH-terminal to or between pairs of basic amino acids, with plasma kallikrein recognizing Lys-Lys, Lys-Arg, and Arg-Arg as processing signals. Moreover, plasma kallikrein was found to cleave at the COOH terminus of the basic pairs of amino acids preceding enkephalin sequences thereby releasing the biologically active form of the peptide with the free NH2-terminal Tyr needed for receptor recognition.
Related Compounds
| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Molecular Formula | Articles |
|---|---|---|---|
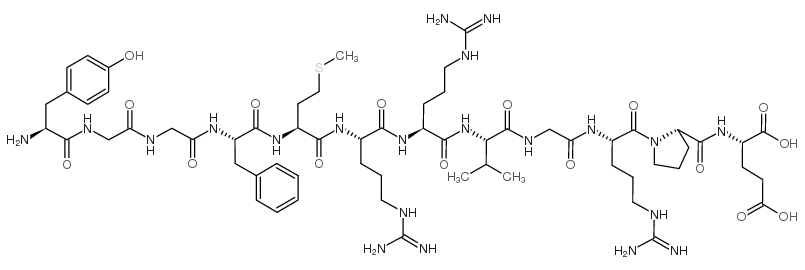 |
Bovine adrenal medulla dodecapeptide
CAS:75513-71-2 |
C62H97N21O16S |
|
Substrate specificity of a novel serine protease from soybea...
1996-06-01 [J. Biochem. 119(6) , 1094-9, (1996)] |
|
Opioid activity of pro-enkephalin-derived peptides in mouse ...
1985-11-11 [Neurosci. Lett. 61(3) , 267-71, (1985)] |
|
A new family of endogenous "big" Met-enkephalins from bovine...
1980-12-31 [Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 97 , 1283, (1980)] |
|
A new endogenous opioid peptide from bovine adrenal medulla:...
1980-08-29 [Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 95 , 1482, (1980)] |
|
[Spatial structure of BAM-12P dodecapeptide and its analogue...
2005-01-01 [Bioorg. Khim. 31(3) , 245-50, (2005)] |