Opioid activity of pro-enkephalin-derived peptides in mouse vas deferens and guinea pig ileum.
P Sánchez-Blázquez, J Garzón
Index: Neurosci. Lett. 61(3) , 267-71, (1985)
Full Text: HTML
Abstract
The inhibitory activity of several pro-enkephalin A-derived opioid peptides, containing the sequence of Met-enkephalin, was evaluated in two isolated organ preparations sensitive to opioids, the guinea pig ileum (GPI) and the mouse vas deferens (MVD). All peptides tested were able to inhibit the electrically stimulated contraction in both tissues by interacting with specific receptors sensitive to the opioid antagonist naloxone. The shorter peptides in this family (Met-enkephalin, Met5-enkephalin-Arg6-Phe7, Met5-enkephalin-Arg6-Gly7-Leu8) displayed their highest potency in MVD. In contrast, the larger bovine adrenal medulla (BAM) peptides (BAM 12P, BAM 22P and peptide E) were more potent in the GPI system compared with the MVD assay. Therefore, the larger peptides seem to bind better to the mu receptor, whereas the shorter ones prefer the delta type.
Related Compounds
| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Molecular Formula | Articles |
|---|---|---|---|
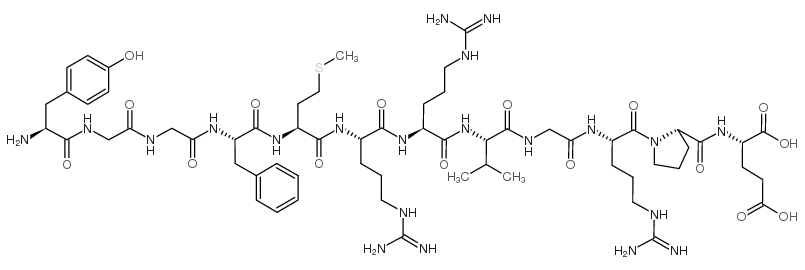 |
Bovine adrenal medulla dodecapeptide
CAS:75513-71-2 |
C62H97N21O16S |
|
Substrate specificity of a novel serine protease from soybea...
1996-06-01 [J. Biochem. 119(6) , 1094-9, (1996)] |
|
A new family of endogenous "big" Met-enkephalins from bovine...
1980-12-31 [Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 97 , 1283, (1980)] |
|
A new endogenous opioid peptide from bovine adrenal medulla:...
1980-08-29 [Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 95 , 1482, (1980)] |
|
[Spatial structure of BAM-12P dodecapeptide and its analogue...
2005-01-01 [Bioorg. Khim. 31(3) , 245-50, (2005)] |
|
Distribution and characterization of opioid peptides derived...
1984-06-18 [Brain Res. 304(1) , 127-36, (1984)] |