[Biotransformation of benzamidine and benzamidoxime by microsomal enzymes of the rabbit].
B Clement, M Zimmermann, S Schmitt
Index: Arch. Pharm. (Weinheim) 322(7) , 431-5, (1989)
Full Text: HTML
Abstract
At pH 7.4 neither benzamidine (1) is ring-hydroxylated nor benzamidoxime (2) is N-hydroxylated, reduced or ring-hydroxylated by aerobic incubations with microsomal fractions (12000 g supernatant, microsomes) of rabbit liver homogenates and NADPH. Products of hydrolytic processes are also not detected. A very long incubation period and a pH 6.3 are necessary for the detection of a slight reduction of benzamidoxime (2) to benzamidine (1). Results are obtained by use of synthetic reference material and by newly developed HPLC methods. Thus, kinetic studies of the microsomal N-hydroxylation of benzamidine (1) to benzamidoxime (2) in the presence of N-methylbenzamidine (3) performed at pH 7.4 are not influenced by other transformations and provide evidence for the involvement of the same isoenzyme of cytochrome P-450 for both the N-hydroxylation of 1 and the N-dealkylation of 3.
Related Compounds
| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Molecular Formula | Articles |
|---|---|---|---|
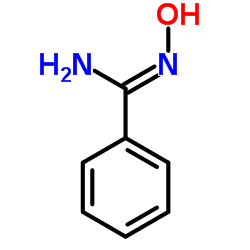 |
N-Hydroxybenzenecarboximidamide
CAS:613-92-3 |
C7H8N2O |
|
A novel and specific fluorescence reaction for uracil.
2010-08-03 [Anal. Chim. Acta 674(2) , 234-8, (2010)] |
|
Characteristics of the microsomal N-hydroxylation of benzami...
1987-06-01 [Xenobiotica 17(6) , 659-67, (1987)] |
|
Biotransformation of benzamidine and benzamidoxime in vivo.
1993-10-01 [Arch. Pharm. (Weinheim) 326(10) , 807-12, (1993)] |
|
Genotoxic activities of benzamidine and its N-hydroxylated m...
1988-01-01 [J. Cancer Res. Clin. Oncol. 114(4) , 363-8, (1988)] |
|
Metabolism of benzamidoxime (N-hydroxyamidine) in human hepa...
2005-01-01 [Xenobiotica 35(1) , 17-25, (2005)] |