| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Articles |
|---|---|---|
 |
3-((Methoxycarbonyl)amino)phenyl m-tolylcarbamate
CAS:13684-63-4 |
|
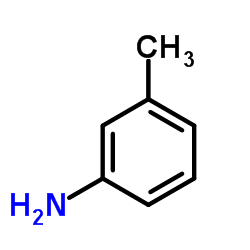 |
3-Toluidine
CAS:108-44-1 |